Figure 2.
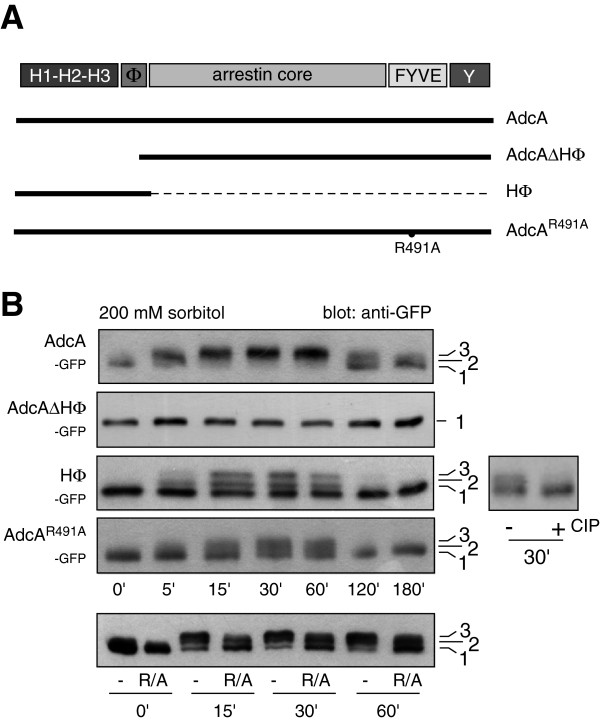
AdcA is phosphorylated on its N-terminal domain. A. Schematic representation of mutants of AdcA. AdcA harbors different domains: a triplicated histidine-rich region (H1-H2-H3), a hydrophobic sequence (Φ), an arrestin core, a FYVE domain and a tyrosine-rich region (Y). Mutants of GFP-tagged AdcA carrying a point-mutation in the FYVE domain (AdcAR491A) preventing endocytic targeting or truncations (HΦ, AdcAΔHΦ) are shown. B. Effect of sorbitol on the migration pattern of AdcA mutants. Cells disrupted for adcA and expressing mutant forms of AdcA were treated with 200 mM sorbitol (t = 0). The impact of the hyperosmotic stress on the electrophoretic migration of the different AdcA mutants was analysed by Western blot using anti-GFP antibodies. To confirm that the shift observed with the HΦ protein was due to phosphorylation, the protein sample was treated with the alkaline phosphatase CIP. On the bottom panel, the samples from adcA null cells overexpressing AdcAGFP or AdcAR491AGFP were loaded side by side to facilitate comparison.