Figure 4. Effect of noise correlation on decoding.
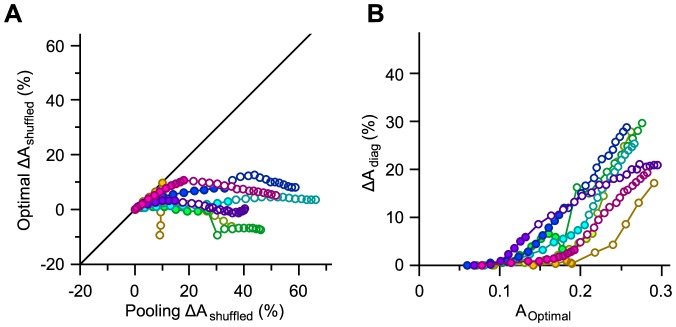
A. The ordinate represents the relative effect of noise correlation. This is captured by the per cent change in the value of A for a groupwise decoder optimized on trial-shuffled neuronal responses. The abscissa indicates the effect of noise correlation on pooling scheme. This is captured by the increase in the value of A for pooling after trial-shuffling neuronal responses. Color conventions and selection of neurons for every population are identical to Figure 2. For every selection of neurons for a given population size, the values of A for 50 trial-shuffles were averaged. B. The effect of ignoring noise correlation when decoding. ΔAdiag corresponds to the per cent drop in the performance of a decoder which ignores noise correlation. Noise correlations were ignored by setting the off-diagonal elements of the total covariance matrix to zero.
