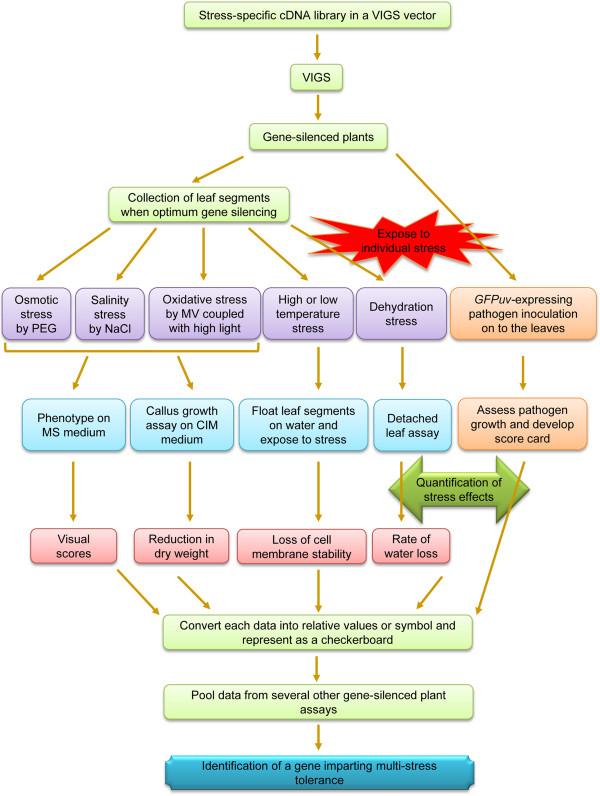
Figure 7.
Proposed VIGS-based high-throughput screen to identify genes involved in multi-stress tolerance in N. benthamiana. A cDNA library from the plants treated with various abiotic stresses can be cloned into pTRV2 vector. This library can be used for a forward genetic screening. TRV-VIGS can be used to silence each of these genes, and the silenced plants can be evaluated for their multi-stress tolerance by using the high-throughput methods described and demonstrated in this manuscript. Leaf disks can be collected from a silenced plant and exposed to specific abiotic stress. Such stress-treated leaf disks can be analysed for stress effects by using various physiological and biochemical assays. Similarly, the silenced plants can be inoculated with pathogens expressing GFPuv and their growth can be visualized by the naked eye under UV light in the dark. Based on this assay, genes involved in basal and nonhost disease resistance can be identified. Finally, relative scores can be assigned in a checkerboard for each of the stress treatments and compared with control plants. This procedure can be followed for a large number of silenced plants and thereby multi-stress tolerant plants can be identified.