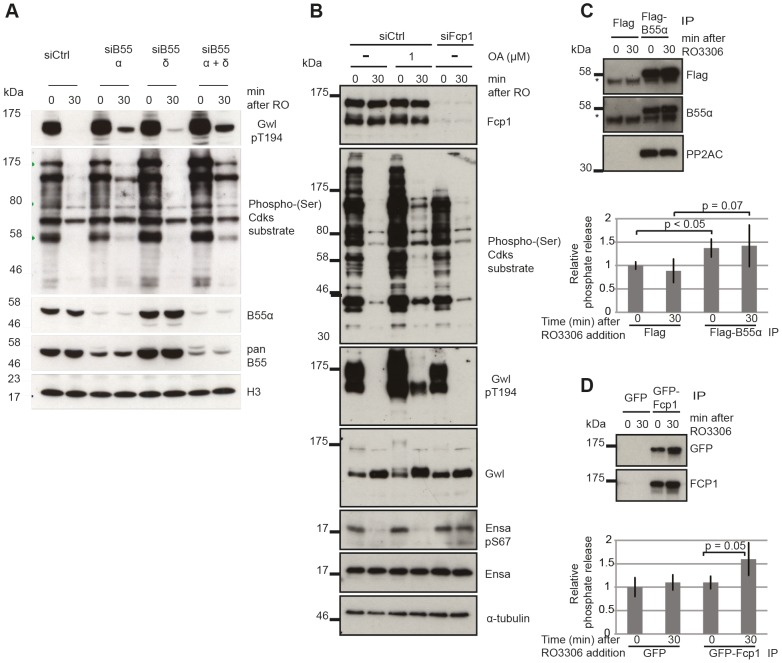
Figure 5. Identifying the phosphatases required for Gwl and Ensa/ARPP19.
(A) Dephosphorylation of Gwl and SP sites in B55 depleted cells. HeLa cells were transfected with combinations of B55α and δ siRNAs and synchronized in mitosis with STLC as above (see Materials & Methods). Cell extracts were sampled before and 30 minutes after RO3306 treatment and analyzed by immuno-blotting with indicated antibodies. (B) Dephosphorylation of Gwl, Ensa/Arpp19 and SP sites in Fcp1 depleted cells. HeLa cells were transfected with Fcp1 siRNA and synchronized in mitosis with STLC (see Materials & Methods). Cell extracts were sampled before and 30 minutes after RO3306 treatment and analyzed by immune-blotting with indicated antibodies. (C) Gwl phosphatase assay with immuno-precipitated Flag-B55α. Purified his-Gwl was phosphorylated by Cdk2/cycA and γ32P ATP. Cdk2/cycA was removed from the reaction by further purification with Ni-Agarose beads and radiolabeled phospho-Gwl was incubated with immunoprecipitated B55α. The presence of the PP2A/B55α complex in the immune-precipitate was confirmed by immuno-blotting. Phosphatase activity was measured by scintillation counting of released [32]P phosphate. (D) Similar phosphatase assay as in (C) with recombinant in vitro phosphorylated Ensa and immuno-precipitated GFP-Fcp1.