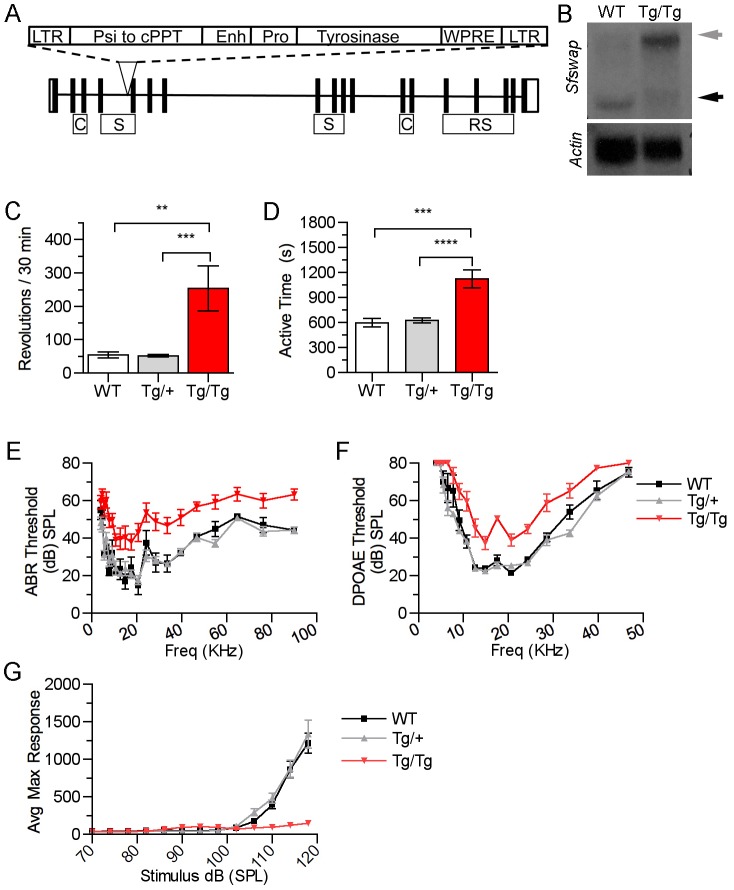
Figure 1. Mutation of Sfswap results in mice with vestibular and cochlear defects.
(A): Lentiviral integration into the 4th intron of Sfswap. The exons of Sfswap are shown with black vertical bars. The features of the lentivirus are indicated as follows: LTR: long terminal repeat, Psi: packaging sequence, cPPT: central polypurine tract, Enh: tyrosinase enhancer, Pro: tyrosinase promoter, WPRE: woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element. Features of the Sfswap gene are indicated as follows: C: Coil-Coil, S: SURP domain, RS: Arginine-Serine domain. (B): Northern blot of brain RNA from wild-type and SfswapTg mice. The mutation caused by the insertion of the lentivirus results in a reduction of wild-type Sfswap transcript (black arrow) and the appearance of a new isoform greater than 10 Kb in size (grey arrow). (C, D): In a 30-minute open field task, SfswapTg mice exhibit increased circling behavior (C) and hyperactivity (D). (E, F): SfswapTg/Tg mice exhibit increased auditory thresholds measured by ABR (E; p(WT, Tg/Tg) = 0.003, p(Tg/+, Tg/Tg) = 2×10−4) (black - WT, grey - Tg/+, red - Tg/Tg) and increased DPOAE thresholds (F; p(WT, Tg/Tg) = 1×10−4, p(Tg/+, Tg/Tg) = 3×10−6), indicating a hearing deficit. (G): SfswapTg/Tg mice show a reduced startle response. Mice were allowed to acclimate to a 70 dB background noise, and were then exposed to noise of increasing sound pressures. Wild type and Sfwap Tg/+ mice begin to show a response at 100 dB, whereas SfswapTg/Tg mice do not begin to show a startle response until 118 dB (p(WT, Tg/Tg) = 2.2×10−7, p(Tg/+, Tg/Tg) = 1.8×10−7).