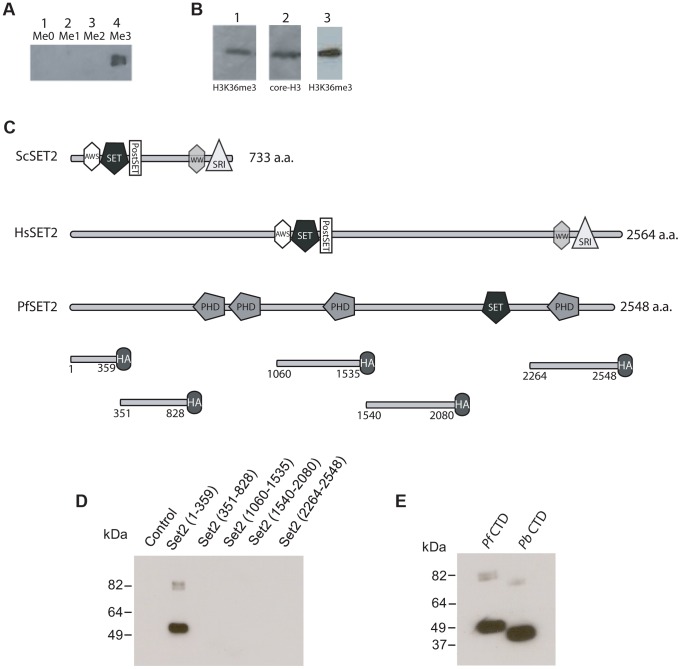
Figure 2. Detection of H3K36me3 in chromatin from P. falciparum and identification of the Rpb1binding region of PfSET2.
(A) Slot blots of the synthetic peptide sequence RKSAPISAGIKKPHRYRPGT. This sequence includes K36 of histone H3 of P. falciparum (underlined). Lane 1, unmethylated peptide. Lane 2, peptide synthesized with a mono-methyl group at the K36 position. Lane 3, peptide synthesized with a di-methyl group at the K36 position. Lane 4, peptide synthesized with a tri-methyl group at K36 position. All lanes included 15 µg of purified peptide. The dot blot was probed with antibodies against the tri-methylated form of the peptide and demonstrated that the antibodies are specific to the tri-methylated form. (B) Western blot of P. falciparum protein extracts taken from early trophozoites. Lane 1, blot of total parasite proteins probed with anti-H3K36me3 antibodies. Lane 2, blot of total parasite proteins probed with anti-H3-core antibodies. Both antibodies recognize bands migrating at ∼18 kDa. Lane 3, blot of acid extracted histones obtained from cultured parasites and probed with anti-H3K36me3 antibodies. (C) Comparison of the architecture of SET2 orthologs from S. cerevisiae, H. sapien and P. falciparum. Note that the SET2-Rpb1-Interacting domain (SRI) is found at the C-terminal end of both the yeast and human SET2 proteins. The protein domains shown in the figure are displayed using the format derived from SMART (Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool, http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de). Below PfSET2 are displayed the portions produced as HA-tagged, recombinant proteins for use in co-immunoprecipitation assays. The numbers below each fragment represent the amino acid positions within the full-length protein. The tandem PHD domains (amino acids 829–1060) were not included because the DNA encoding the this region of the protein was unstable in the expression vector. The SET domain was also not included because the structure and function of this domain is conserved and was previously shown not to bind the CTD in yeast and human systems. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation assays used to identify the region of PfSET2 that interacts with the CTD of Rpb1. Flag-tagged fragments of the CTD of Rpb1 shown in E were incubated with bacterial lysates containing the truncates of PfSET2 shown in C. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-HA beads followed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-Flag antibodies. Only the most N-terminal portion of PfSET2 (amino acids 1–359) was found to interact with the CTD of Rpb1. The control reaction consisted of an HA-tagged PHIST protein similarly incubated with the CTD of Rpb1. (E) The N-terminal region of PfSET2 also binds to Rpb1 regions with fewer numbers of repeats. Co-immunoprecipitation assay performed as in D, using either the CTD of Rpb1 from P. falciparum (left lane) or P. berghei (right lane). The P. berghei CTD has only 8 heptad repeats.