FIGURE 2.
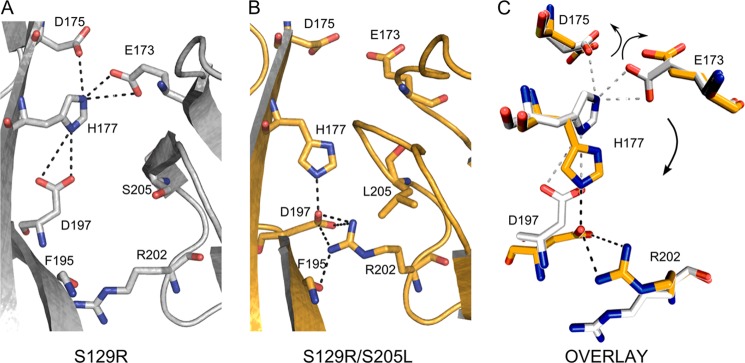
Structural changes produced by the S205L mutation. A, magnification of the intersubunit connections in the S129R mutant structure. Here, His177 engages with Glu173 and Asp175 to form a triad that may stabilize the tetrameric structure. B, magnification of the intersubunit interactions in the S129R/S205L mutant. In this structure, His177 has changed its rotamer conformation and interacts with Asp197. Also, a novel interaction is observed between Asp197 and Arg202. His177, Asp197, and Arg202 form a novel triad of interactions at the cytoplasmic domain interface. C, alignment of subunit interface residues of the S129R mutant (gray) and the S129R/S205L mutant (gold). When His177 is engaged with Glu173 and Asp175, these residues are located within the intersubunit space. By contrast, when His177 switches its rotamer conformation and interacts with Asp197 and Arg202, Glu173 and Asp175 are released from the intersubunit space and line the cytoplasmic pore.
