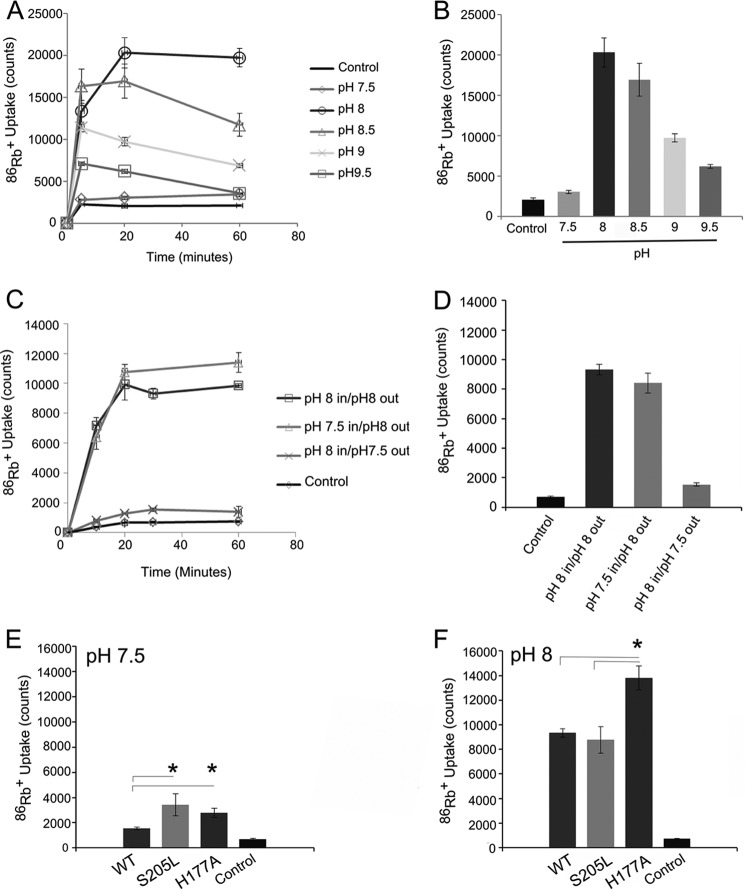
FIGURE 5.
KirBac3.1 is a pH-sensitive channel. A, time course of 86Rb+ uptake at different pH values over 60 min. B, comparison of 86Rb+ uptake after 20 min at different pH values. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3). Channel activity reached a maximum at pH 8.0 and steadily decreased as the pH became more alkaline. C and D, the pH sensitivity is one-sided. Full activity of the channel could be obtained by changing only the extraliposomal pH to 8, whereas adjusting the internal pH to 8 resulted in low channel activity. This indicates that the majority of the channels are oriented uniformly in the liposomes and that the pH sensitivity originates from the side of the channel facing the external solution. The data are presented as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3) for all time points. E and F, steady-state 86Rb+ uptake of WT KirBac3.1 compared with S205L and H177A at pH 7.5. Both S205L and H177A increased the activity of the channel, but neither abolished the pH sensitivity of the channel. Mutation S205L appeared to be functionally silent at pH 8 compared with the WT channel. Mutation H177A remained more active than both the wild-type channel and the S205L mutant. Error bars represent S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05.