FIGURE 3.
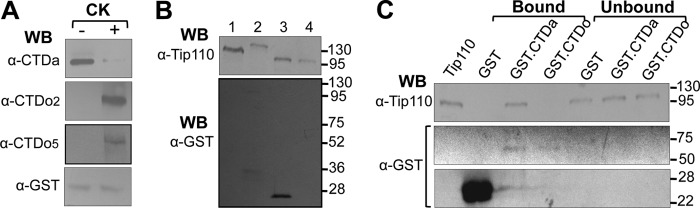
Direct binding of Tip110 to RNAPII CTDa. A, GST-CTDa protein was expressed and purified from E. coli and phosphorylated by casein kinase I (CK) in vitro. GST-CTDa and CK-phosphorylated GST-CTD (GST-CTDo) were confirmed by Western blot analysis with α-CTDo, α-CTDo2, α-CTDo5, or α-GST antibody. Western blot analysis against GST was included as a loading control. B, GST-Tip110 protein was expressed and purified from E. coli (lane 2). Its GST tag was removed by thrombin digestion (lane 3), followed by glutathione bead affinity purification to remove the GST tag (lane 4). All of those proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis with α-Tip110 antibody or α-GST antibody. WCE from 293T cells were included as a control (lane 1). C, GST-CTDa, CK-phosphorylated GST-CTD (GST-CTDo), and GST proteins were immobilized with 50 μl of glutathione beads and then incubated with purified Tip110 protein. The beads and the supernatants were separated by centrifugation and collected to represent bound and unbound fractions, respectively. The beads were then subject to repetitive washes to remove unbound proteins. Then the proteins bound on the beads and in the supernatants were detected by Western blot analysis with α-Tip110 antibody. Purified Tip110 protein was included as the control to indicate the correct protein size (lane 1). The membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti-GST antibody to ensure GST binding to the glutathione beads.
