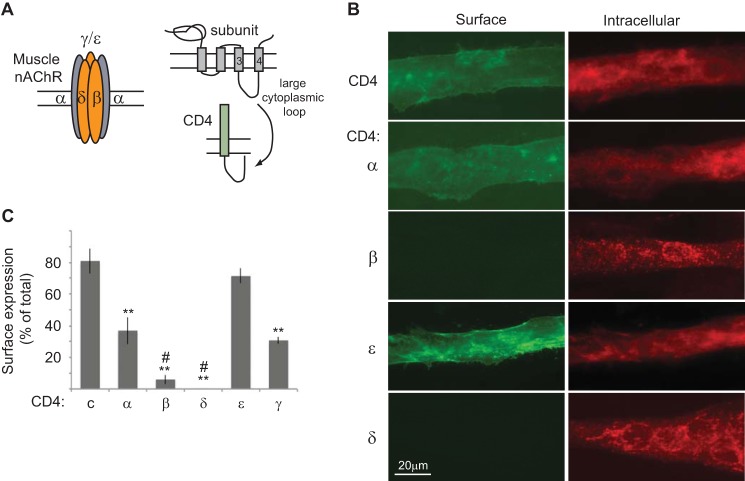
FIGURE 1.
Cellular localization of CD4-AChR subunit loops in muscle cells. A, schematic shows the subunit composition of muscle AChR, the topology of each subunit, and the CD4-subunit cytoplasmic loop chimeras used to screen for post-ER trafficking signals. B, C2 myotubes transfected with CD4-subunit loops were fixed and immunostained for surface CD4 chimeras with anti-CD4 antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody (green). The cells were then permeabilized and immunostained for intracellular chimeras with anti-CD4 and Alexa Fluor 594 secondary antibody (red). CD4 and CD4-α and ϵ loops were expressed on the cell surface, whereas CD4-β and δ loops were retained intracellularly. C, quantification of surface expression of each CD4-subunit loop was done by on-cell Western blot assays. A high percentage of CD4 and CD4-ϵ loops and moderate percentage of CD4-α and γ loops were expressed on the cell surface. In contrast, only 6% of CD4-β and 0.3% of CD4-δ loops were detectable on the plasma membrane; thus, they are almost exclusively localized in the intracellular compartment.**, p < 0.01 compared with CD4 and CD4-ϵ; #, p < 0.05 versus CD4-α; ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. Error bars, S.E.