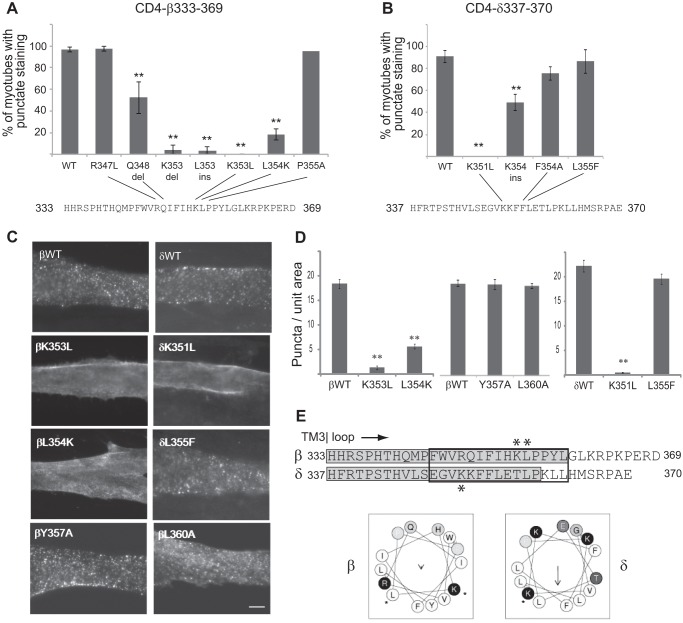
FIGURE 5.
Internalization is mediated by novel motifs that include lysine residues. A series of mutations was introduced in the proximal β and δ loop regions, and their internalization was assayed. A, C, and D, endocytosis of CD4-β(333–369) was decreased significantly by K353L and L354K mutations or by insertions (ins) or deletions (del) at these positions (**, p < 0.01 compared with β(333–369) wild type (WT), R347L, and P355A; ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Error bars, S. E. In contrast, mutation of the putative YXXL motif (βY357A and L360A) did not inhibit internalization. B–D, endocytosis of CD4-δ(337–370) was inhibited by K351L and K354ins mutations. C, scale bar, 10 μm. E, sequence alignment of the proximal regions of β and δ loops is shown, with the minimal retention signals highlighted in gray, and asterisks marking the position of mutations that blocked internalization. For both subunits the critical determinants include lysine residues in predicted α-helixes (black box) with similar arrangements of hydrophobic and charged residues (helical wheel projection).