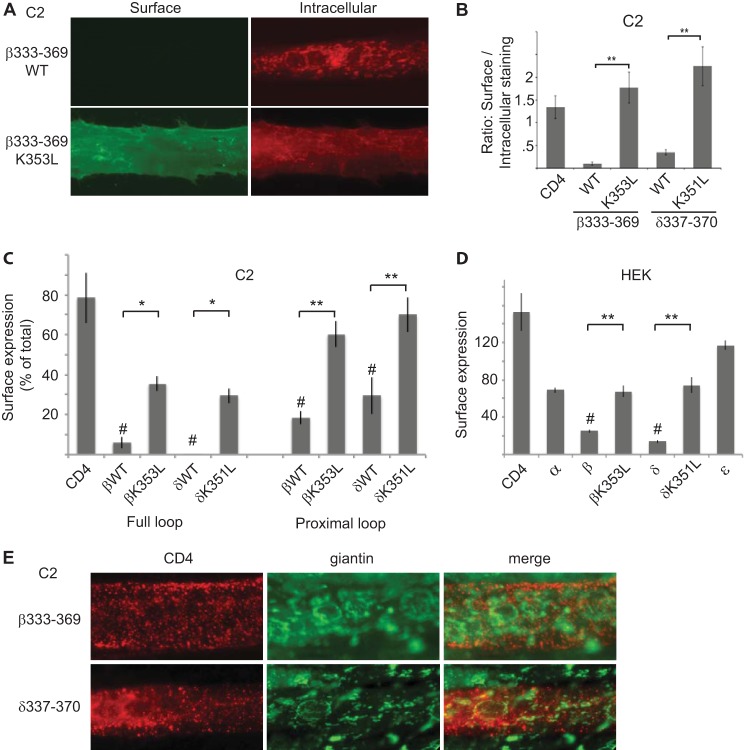
FIGURE 6.
Golgi retention is mediated by the same sequence determinants that mediate internalization. A, C2 muscle cells transfected with CD4-β(333–369) were immunostained sequentially for surface and intracellular CD4 chimeras. CD4-β(333–369) wild type (WT) was mostly retained intracellularly in the Golgi complex, whereas CD4-β(333–369) K353L was robustly expressed on the cell surface. B, quantification shows that βK353L and δK351L mutations resulted in a significantly higher ratio of surface to intracellular staining compared with WT (**, p < 0.01, ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Error bars, S.E. C, C2 muscle cells were transfected with CD4-β and δ loop chimeras, and the percentage of each protein that was expressed on the cell surface was determined in on-cell Western blot assays. Like CD4-β and δ full loops, CD4-β(333–369) and δ(337–370) were expressed on the cell surface at much lower levels than CD4 (#, p < 0.01, ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Moreover, surface expression was increased significantly by βK353L and δK351 mutations (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05, ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test, n = 3–6 independent experiments). D, in analogous experiments in HEK cells, CD4-β and δ loops were expressed on the cell surface at significantly lower levels than CD4 (#, p < 0.01, ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test), and their surface expression was increased significantly by K353L and K351L mutations, respectively (**, p < 0.01, ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Thus, the retention/retrieval signals are also recognized in heterologous cells. E, C2 muscle cells transfected with CD4-β(333–369) or δ(337–370) were labeled with anti-CD4 antibody live for 10 min and then chased for 2 h. Co-staining for CD4 and giantin shows that the internalized CD4-β and δ chimeras remain in punctate-vesicular structures and do not traffic back to the Golgi complex. Together, these findings show that the β and δ subunit proximal loops mediate both Golgi retention and retrieval from the plasma membrane, via similar sequence determinants.