FIGURE 7.
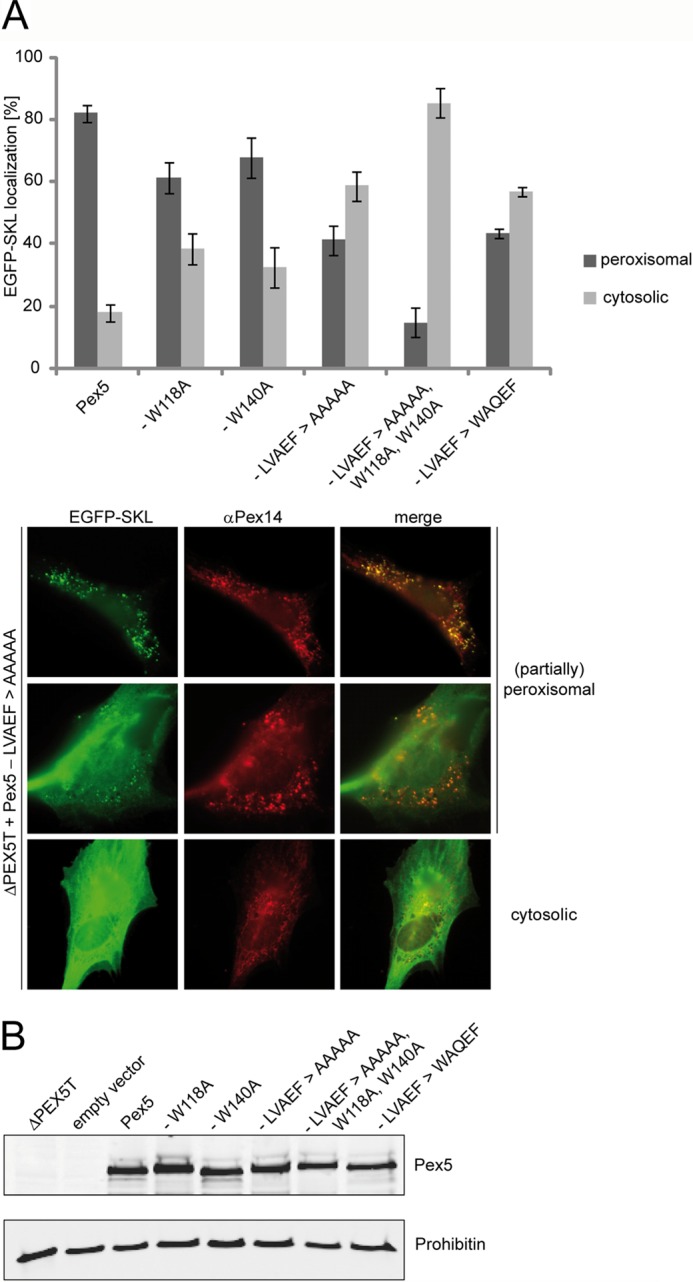
Functional complementation of PEX5-deficient fibroblasts by Pex5 carrying mutations in distinct Pex14-binding sites. Full-length Pex5 was mutagenized either in single Pex14-binding sites by alanine substitution of the LVXEF motif (LVAEF > AAAAA), the first (W118A), or the second (W140A) WXXX(F/Y) motif, or in combination (LVAEF > AAAAA, W118A,W140A). Furthermore, the LVXEF motif was substituted by the first WXXX(F/Y) motif, indicated by LVAEF > WAQEF. All constructs were expressed in Pex5-deficient fibroblasts (ΔPEX5T) from bicistronic expression vectors coding for the full-length Pex5 variants as indicated and EGFP fused to a PTS1 (EGFP-SKL). A, localization of the peroxisomal matrix marker protein EGFP-SKL was monitored by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies against EGFP. Peroxisomes were labeled in red by immunofluorescence microscopy of the peroxisomal membrane marker Pex14. Representative cells expressing the Pex5-LVAEF > AAAAA mutant are shown in the lower panel. A congruent punctate red and green fluorescent pattern indicates partial or complete restoration of peroxisomal protein transport, whereas diffuse cytosolic staining of EGFP-SKL shows that the protein is at least partially mislocalized to the cytosol, indicating a low complementation activity of transfected Pex5 variant. The graph shows a quantitative analysis of mutant phenotype complementation by the individual Pex5 variants. Values were obtained from three or six independent transfection experiments. For each experiment, 100 transfected cells were categorized into those enabling EGFP-PTS1 import (peroxisomal) and those without complementation of the import defect (cytosolic). B, immunoblot analysis shows that all Pex5 variants are present at the same steady-state level as the plasmid-encoded full-length wild-type Pex5. Negative controls show lysates of cells either nontransfected or transfected with empty vector (pIRES2). The analysis of prohibitin served as loading control.
