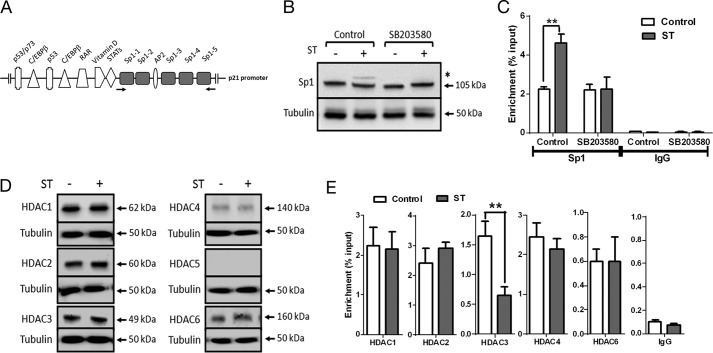
FIGURE 4.
Sp1 and HDAC3 are required for cGMP-dependent p21 transcription. A, transcription factor binding sites on the proximal p21 promoter (34). The Sp1 binding sites are highlighted, and the arrows indicate primers used for ChIP analysis. C/EBP, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein; RAR, retinoic acid receptor. B, Western blot analysis of Sp1 upon ST stimulation (100 nm) in T84 cells treated with SB203580 (10 μm). * marks the lower mobility form of Sp1. C, ChIP-quantitative PCR demonstrating enhanced Sp1 binding to the p21 promoter upon treatment with ST (100 nm). Treatment with SB203580 (10 μm) abrogated this increase in Sp1 binding. IgG represents normal goat IgG, which was used as a control in ChIP analysis. Values shown represent the mean ± S.E. of experiments repeated thrice (**, p < 0.01). D, Western blot analysis of lysates of T84 cells treated with ST (100 nm) for 1 h with HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC6 antibodies. E, ChIP-quantitative PCR to estimate occupancy of the indicated HDACs on the p21 promoter upon treatment with ST (100 nm). NMI represents normal mouse IgG and NRI represents normal rabbit IgG used as controls for HDAC1–3 antibodies and HDAC4–6 antibodies, respectively, during ChIP analysis. Values shown represent the mean ± S.E. of experiments repeated thrice (**, p < 0.01). Error bars represent S.E.