FIGURE 9.
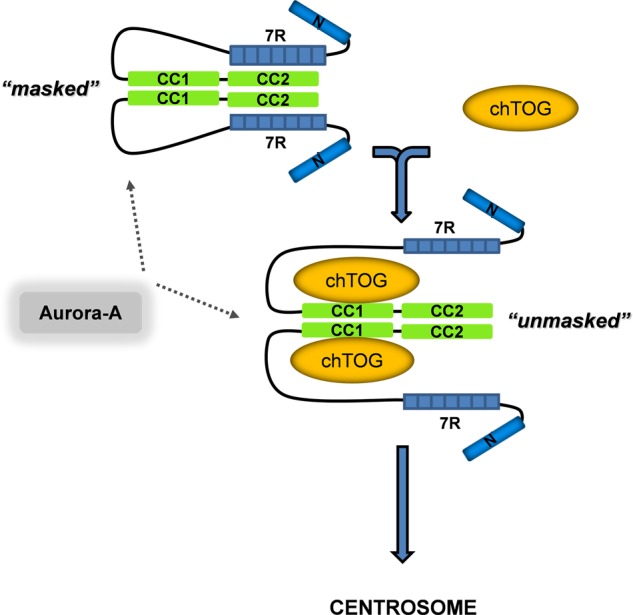
Integrative model for the domain specificity and directionality of TACC3-chTOG complex formation. We propose that the intradomain (7R-CC2; TACC3 masked) and intermolecular (CC1-chTOG; TACC3 unmasked) binding states of TACC3 are mutually exclusive, thereby defining a directionality of TACC3 regulated adaptor function toward chTOG binding and function. TACC3 can be phosphorylated by Aurora-A kinase in both binding states, indicating that Aurora-A acts as a centrosomal recruitment factor but is not involved in exposing the TACC domain for intermolecular interaction with chTOG or TACC3-chTOG complex formation. Moreover, based on biophysical characterization of murine TACC3 (supplemental Fig. 11, B and C, and supplemental Table S1; Ref. 34) we conclude that TACC3 displays an dimeric to oligomeric state. Thr., thrombin.
