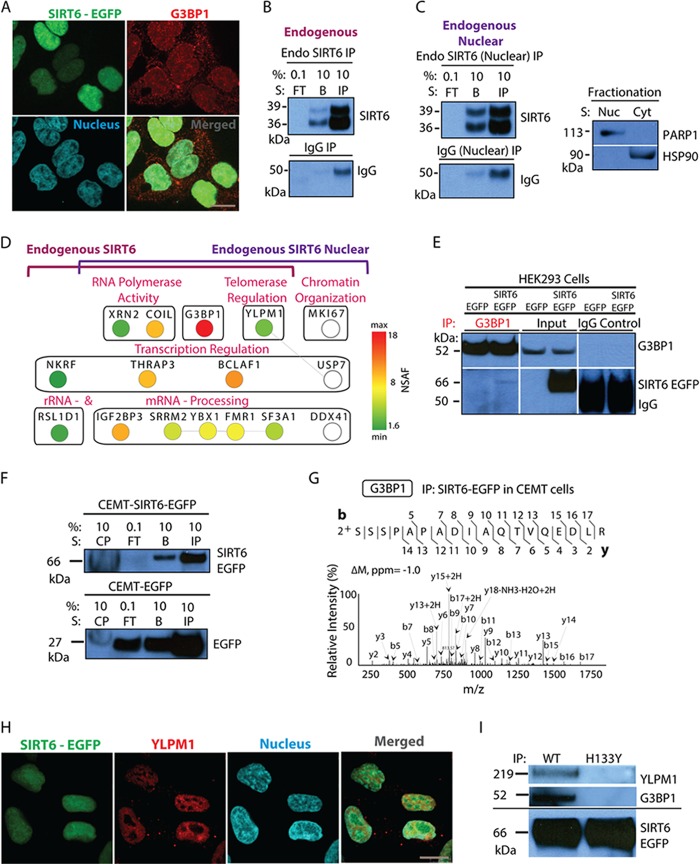
Fig. 7.
SIRT6–G3BP1 interaction occurs in different cell types and is dependent on the catalytic activity of SIRT6. A, confocal microscopy revealed the nuclear and cytoplasmic distribution of G3BP1 and demonstrated nuclear co-localization with SIRT6-EGFP; EGFP-tagged SIRT6 (green), G3BP1 (red, anti-G3BP1 antibody), nucleus (blue, DAPI staining), 60× oil immersion lens, 2× optical zoom, scale bar = 10 μm. B, endogenous SIRT6 is isolated from whole cell lysates of wt HEK293 cells as shown by WB analysis (FT, flow through; IP, primary protein elution; B, secondary protein elution). Control IgG isolations were used as a negative control. C, IP of endogenous SIRT6 performed after nuclear fractionation. WB analysis showed bait isolation using antibodies against SIRT6 and IgG (left). Successful nuclear/cytoplasmic fractionation was demonstrated by WB with anti-PARP1 and -HSP90 antibodies, used as nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively (right). D, mass spectrometry and bioinformatics analyses of endogenous SIRT6 isolations. Cytoscape network generated for overlapping whole cell and nuclear fractionation interactions comprised proteins with more than five spectrum counts and at least 3-fold enrichment relative to IgG. Node color reflects NSAF values. White nodes indicate interactions identified only in the nuclear fractionation endogenous IP (set not analyzed by NSAF). Edge lines represent known protein clusters. E, reciprocal IP using anti-G3BP1 antibody revealed co-isolation of EGFP-tagged SIRT6 in HEK293 cell lines expressing the tagged protein. Parallel IgG isolations and IPs from HEK293-EGFP cells served as negative controls. WB analyses of reciprocal IP samples were performed with antibodies against G3BP1 (top) and SIRT6 (bottom). F, G, association between SIRT6 and G3BP1 occurred in CEMT cells. F, SIRT6-EGFP was efficiently isolated (CP, insoluble cell pellet; FT, flow through; IP, primary protein elution; B, secondary protein elution). G, association between SIRT6 and G3BP1 was observed in CEMT cells. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed G3BP1 as a constant SIRT6 binding partner (CID MS/MS using nano-LC LTQ Orbitrap Velos). H, YLPM1 co-localizes with SIRT6-EGFP in the nucleus of HEK293 cells. Confocal microscopy was performed using direct fluorescence for SIRT6-EGFP (green), antibodies against YLPM1 (red), and nuclear staining (blue, DAPI), with a 60× oil immersion lens and 2× optical zoom; scale bar = 10 μm. I, isolation of wt and H133Y SIRT6-EGFP confirmed the dependence on the SIRT6 catalytic activity for the associations with G3BP1 and YLPM1.