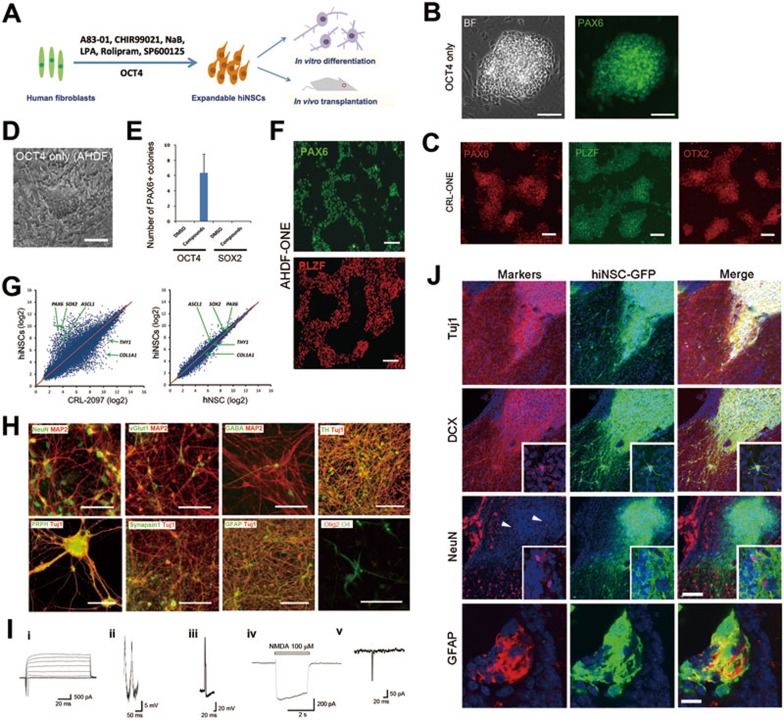
Figure 1.
hiNSC reprogramming with OCT4 and small molecules. (A) Reprogramming conditions for the generation of hiNSCs. Human fibroblasts were transduced with OCT4 alone and cultured for 28-35 days with small molecules. The details are described in the Supplementary information, Data S1. (B) Representative images of hiNSC colonies reprogrammed from CRL-2097 transduced with OCT4 alone, and immunostained with PAX6. BF, brightfield. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) Immunostaining of isolated and expanded hiNSC colonies (at passage > 5) reprogrammed from CRL-2097 with OCT4 alone (CRL-ONE). PAX6 (left), PLZF (middle) and OTX2 (right) are expressed homogeneously in all cells. Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) Reprogramming of AHDF. Brightfield image of a hiNSC-like colony. Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) Histogram showing the number of PAX6-positive colonies generated by direct reprogramming of AHDF transduced with OCT4 or SOX2 alone and cultured for 35 days with small molecules (n = 3). (F) Immunostaining of isolated and expanded hiNSC colonies (at passage > 5) reprogrammed from AHDF transduced with OCT4 alone (AHDF-ONE) and cultured for 35 days with the chemical cocktail. PAX6 and PLZF are expressed homogeneously in all cells. Scale bars, 100 μm. (G) Scatter plots comparing the global gene-expression patterns between hiNSCs and human fibroblasts (CRL-2097) or control hNSCs. The positions of the neuro-ectodermal genes PAX6, ASCL1 and SOX2, as well as fibroblast genes COL1A1 and THY1, are indicated by arrows. (H) Representative images of immunostained neuronal and glial cells differentiated from hiNSCs. These differentiated hiNSCs exhibited immunoreactivity to markers of mature neurons, neuronal subtypes, peripheral neurons and glias. Markers are indicated in each image. Scale bars, 100 μm. (I) Electrophysiological properties of hiNSC-derived neurons. (i) Representative trace of fast sodium current evoked by a series of depolarizing pulses. (ii, iii) Representative traces of spontaneous (ii) and evoked (iii) action potentials, as detected by whole-cell recording in current-clamp mode. Action potentials were detected after 5-6 weeks in culture. (iv) Whole-cell NMDA current. (v) sEPSCs recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV, indicating synapse formation. (J) Representative images of hiNSCs transplanted into the lateral ventricle of neonatal (P2 - P3) mice. After 4 weeks, a majority of hiNSCs differentiated into neuronal lineage cells expressing Tuj1 and DCX with extensive arborization, and insets show multiple processes with DCX expression. Some neuronal cells matured into NeuN-expressing neurons within cell clusters (arrowheads), and insets are large magnification views showing NeuN and GFP double-labeled cells. All markers were labeled with red, and nuclei were counter-stained with Hoechst33342 in blue. In some clusters of transplanted hiNSCs, differentiated glial lineage cells expressing GFAP were also found. Scale bars, 50 μm for the upper 3 lanes, 10 μm for the last lane.