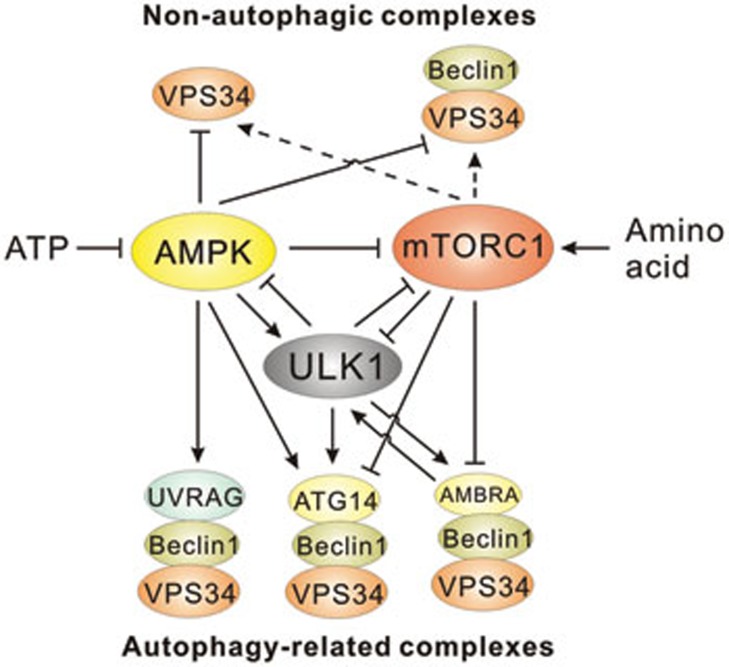
Figure 3.
Regulation of ULK1 and VPS34 complexes by nutrients and upstream kinases. Nutrient starvation activates ULK1 through AMPK-mediated phosphorylation or loss of mTORC1-mediated repression. Activation of ULK1 has been described to initiate a positive-feedback loop through the phosphorylation of the mTORC1 complex and a negative-feedback loop through the phosphorylation of AMPK. Activities of the core VPS34 complexes, containing VPS34 and VPS15 (depicted as VPS34 in all complexes), and Beclin-1-bound VPS34 are inhibited under starvation. AMPK-mediated repression of these complexes is caused by direct phosphorylation of the VPS34 catalytic subunit. Amino acid-induced activation of these complexes is mTORC1-dependent but not direct and does not involve ULK1 kinase. ATG14-containing VPS34 complexes are activated by AMPK or ULK1 through phosphorylation of Beclin-1 or can be inhibited by mTORC1-mediated phosphorylation of ATG14. UVRAG-containing VPS34 complexes are activated by AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of Beclin-1 in response to starvation. ULK1 phosphorylates AMBRA1, freeing VPS34 from the cytoskeleton to act at the phagophore. AMBRA1 acts in a positive-feedback loop with TRAF6 to promote ULK1 activation.