Fig. 1.—
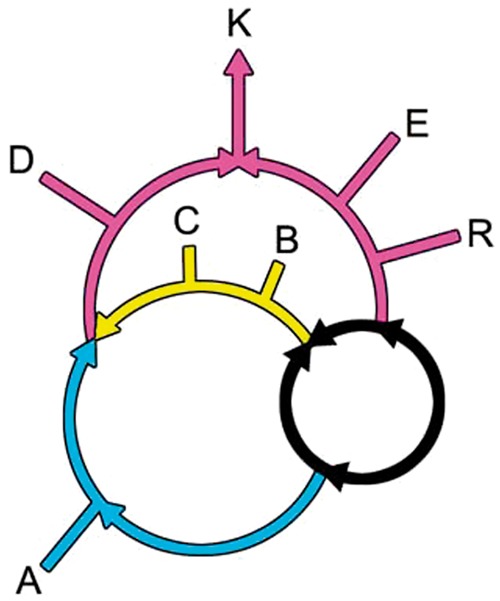
The rooted rings of life consist of an outer, a middle, and an inner ring. The outer ring, shown in pink, resulted in the origin of the eukaryotes (K) through gene flows from the DM prokaryotes (D) on the left and from the eocytes (E) on the right (Rivera and Lake 2004). The DM prokaryotes (D) originated in the middle ring when gene flows from the Actinobacteria, shown in blue, and the Bacilli and the Clostridia, shown in yellow, endosymbioticaly converged (Skophammer et al. 2007; Lake 2009). The previously unknown inner ring, shown in black, contains the root of the rings of life.
