Fig. 3.—
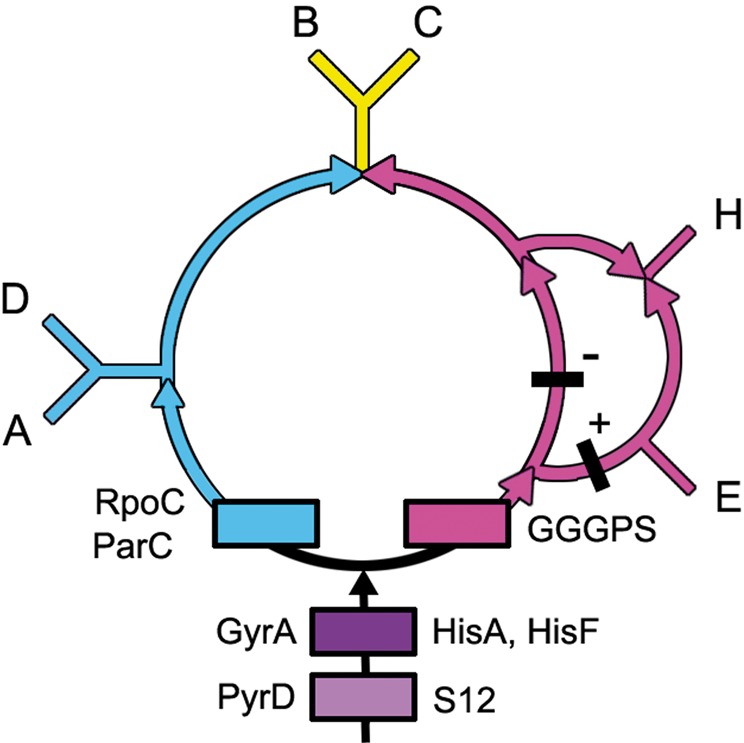
Gene gain sites are shown for eight of the genes analyzed here. Four orthologous genes, PyrD, HisA, HisF, and GGGPS, code for enzymes responsible for building nucleotides, amino acids, and lipids. PyrD codes for the enzyme that performs the final, critical step needed to make the first pyrimidine, Orotate. The gene products of HisA and HisF perform two decisive steps in the synthesis of the amino acid histidine, and GGGPS codes for the penultimate enzyme in the ether lipid biosynthesis pathway. Ribosomal genes S12 and RpoC are orthologous. Ribosomal protein S12 participates in maintaining the fidelity of mRNA translation and the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, RpoC, transcribes RNAs from DNAs. ParC and GyrA are orthologous and code for topoisomerases. Thus, these genes are representative of the fundamental cellular processes of membrane, protein, RNA, and DNA synthesis. Shown in black are the locations of two GGGPS indels. All the indels within the genes used to construct the rooted central ring support this topology. See supplementary section S2, Supplementary Material online, for gene alignments, orthologs, and indels.
