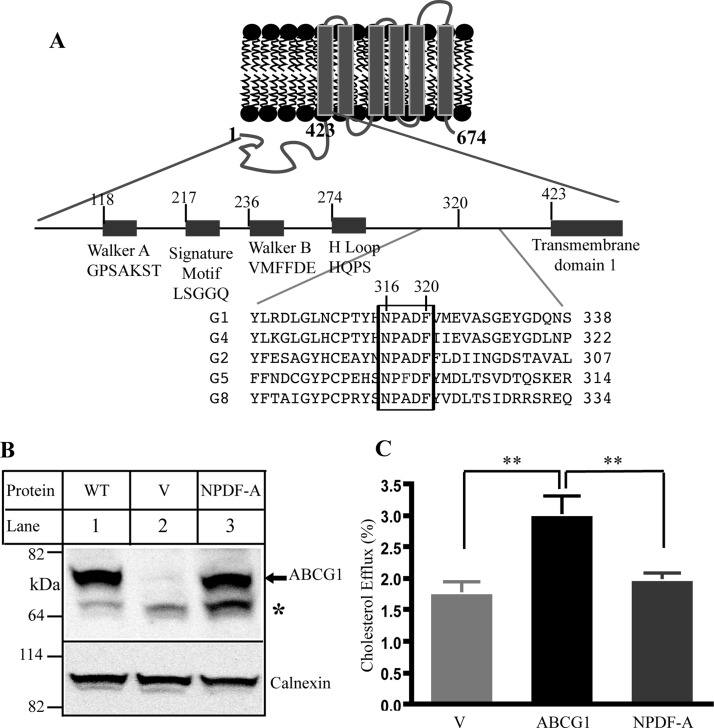
Figure 1.
Effect of the conservative sequence on ABCG1 function. Panel A: Predicted topology of ABCG1 and sequence alignment for ABCG family. Only part of sequence alignment that includes the conserved sequence (NPADF) is shown. The sequence alignment was performed by ClustalW2. Panel B: Expression of wild type and mutant ABCG1. Whole cell lysates were made from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with empty vectors (V) or vectors containing wild type ABCG1 (WT) or mutant ABCG1 (NPDF-A) cDNA and then subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Membrane was cut into halves along the 82 kDa based on the prestained protein standards (Life technology). The bottom part was probed with a polyclonal anti-ABCG1 antibody, H-65 (Santa Cruz), and the top part was detected with a polyclonal anticalnexin antibody. Antibody binding was detected using horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat antimouse or with donkey antirabbit IgG (Sigma) followed by enhanced chemiluminescence detection (Pierce). The membranes were then exposed to Kodak BioMax MR films (Kodak). * indicates no specific band. Panel C: Cholesterol efflux. ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux onto lipidated apoA-I was carried out as described in Materials and Methods. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with empty vector (V) or plasmid containing cDNA of wild type or mutant ABCG1, NPDF-A, in which Asn316, Pro317, Asp319, and Phe320 were replaced with Ala simultaneously. The cells were then labeled with [3H]-cholesterol. After washing, the cells were incubated with 5 μg/mL lipidated apoA-I. The radioactive content of the media and cells was measured separately. Sterol transfer was expressed as the percentage of the radioactivity released from the cells into the media relative to the total radioactivity in the cells plus media. * indicates p < 0.05; ** indicates p < 0.01. Values are mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments.