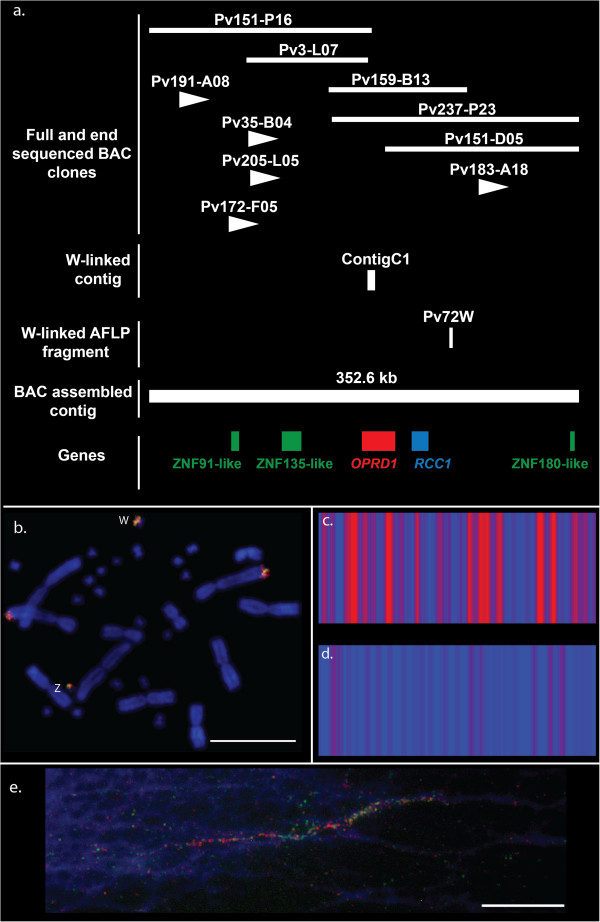
Figure 1.
Isolation and physical mapping of sex chromosome BAC clones in Pogona vitticeps. a: schematic representation of 352 kb partial sex chromosome contig showing relative locations (not to scale) of fully and end sequenced BAC clones, previously identified W-linked contig and AFLP marker, proteins and genes; b: two colour FISH showing locations of two sex chromosome BAC clones at either end of the P. vitticeps 352 kb contig (Pv151_P16 green and Pv151_D05 orange; yellow denotes overlapping signals). Hybridization signal differences between Z and W chromosomes are visible; c: scalable vector graphics (SVG) plot (generated by Repbase-GIRI [48]) of sex chromosome BAC clone Pv03_L07, high density and frequency of red vertical bars represent distributions and locations of repetitive sequences; d: SVG plot of autosomal BAC clone Pv176_G09 showing low frequencies of red vertical bars indicating accumulation of low number of repeats compared to that of the sex chromosome BAC clone; e: two colour fiber FISH (Pv151_P16 orange, Pv237_P23 green), showing orange and green regions and regions of overlap (yellow). Scale bars represent 10 μm.