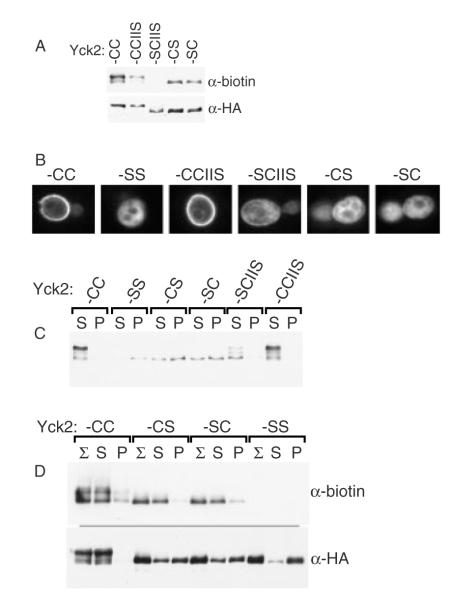
Figure 9.
Use of the glass bead aggregation to analyse the fractional palmitoylation of singly-lipidated Yck2 mutants. (A) Palmitoylation of the singly-lipidated Yck2 mutants. Protein extracts prepared from cells expressing (2 h GAL1-driven expression) either wild-type Yck2 or the indicated mutant versions were analysed for palmitoylation, using the ABE method (see Materials and methods). Palmitoylation is assessed as the intensity of the anti-biotin Western blot signal relative to signal derived from immuno-precipitated Yck2 protein (anti-HA). (B) The subcellular localization of the indicated Yck2 mutant proteins was analysed by anti-HA indirect immunofluorescence, as described for Figure 4B. (C) Glass bead fractionation. Cells expressing the indicated Yck2 mutant proteins from the GAL1 promoter were subjected to glass bead lysis/fractionation as described for Figure 1A. (D) Palmitoylation of supernatant- vs. pellet-fractionated populations. Following the glass bead lysis and centrifugal fractionation described for Figure 9C, supernatant- and pellet-fractionated proteins were subjected to ABE palmitoylation analysis