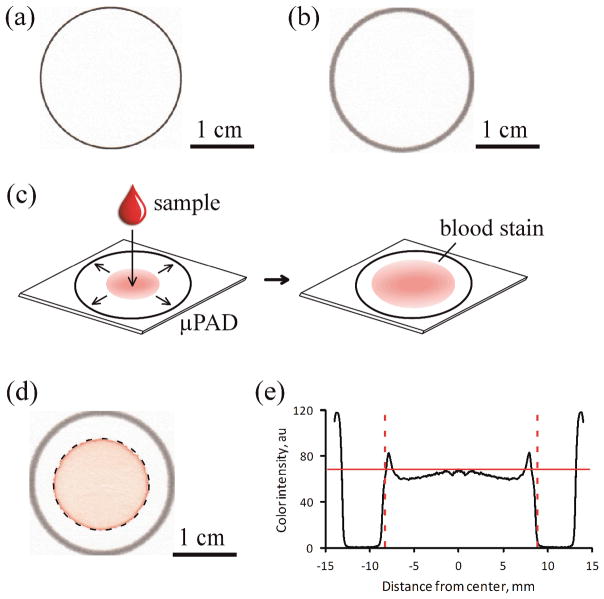
Figure 1.
Design and fabrication of the paper-based Hb assay. (a) The pattern of the μPAD was printed with a solid-ink (wax) printer on chromatography paper. (b) The printed pattern was melted to create a 1 mm-wide hydrophobic barrier spanning the entire thickness of the paper substrate. (c) To perform the assay, a drop of blood mixed with Drabkin’s reagent was placed onto the center of the device. The lysate wicked laterally towards the periphery, coloring the paper faint red (pink). (d) The image analysis algorithm automatically detected the blood stain within each μPAD (dashed circle) and extracted the RGB color information for all pixels contained within the blood stain. (e) The color intensity of the pixels (between dashed lines) was averaged to calculate the mean color intensity (solid red line) for each blood stain. The values of the mean color intensity were used to calculate the [Hb] in the blood samples.