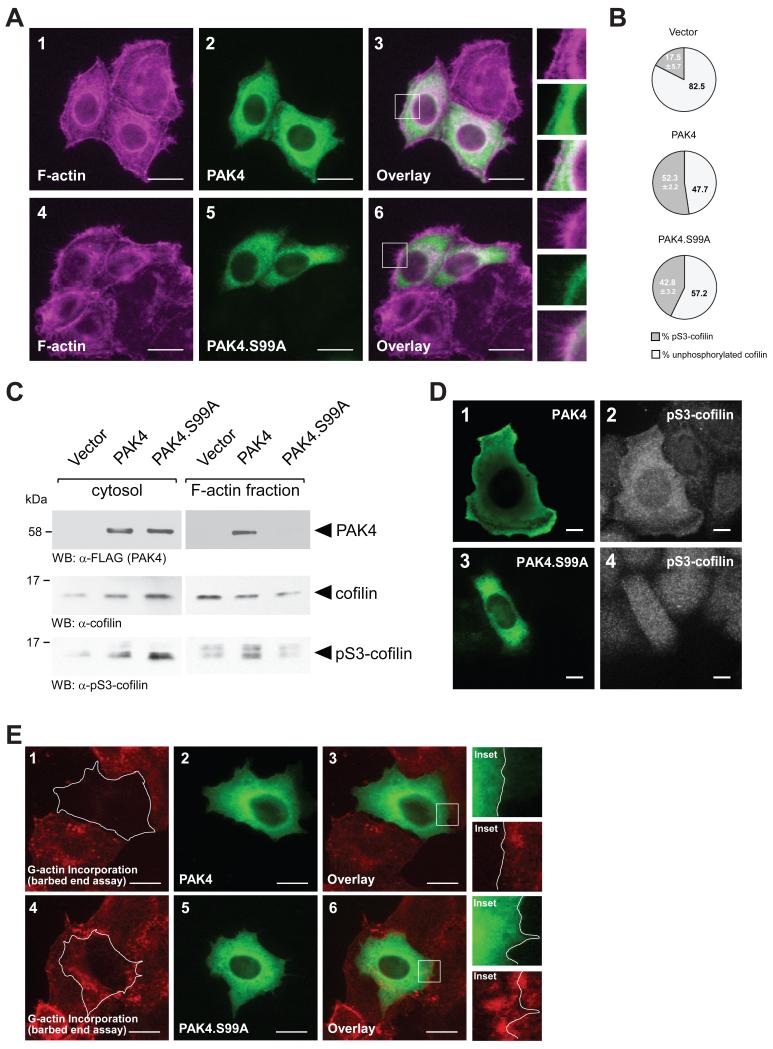
Figure 5. Loss of S99 phosphorylation decreases cofilin phosphorylation at the leading edge.
A. HeLa cells were transfected with wildtype PAK4 or PAK4.S99A mutant. 24 hours after transfection, cells were fixed and PAK4 was stained by immunofluorescence (α-FLAG). F-actin was stained with phalloidin. The insert shows an area at the leading edge of cells. The bar represents 20 μm. B. HeLa cells were transfected with control vector, wildtype PAK4 or PAK4.S99A mutant. Total cell lysates (n=5 experiments) were analyzed by Western blot for cofilin phosphorylation (α-pS3-cofilin antibody) or total cofilin (α-cofilin). Percentage of S3-phosphorylated cofilin and unphosphorylated cofilin was calculated and depicted in a pie graph. C. HeLa cells were transfected with control vector, wildtype PAK4 or PAK4.S99A mutant. Cytosolic and F-actin fractions were prepared and analyzed by Western blot for presence of PAK4 (α-FLAG), or presence of endogenous cofilin or pS3-cofilin. D. HeLa cells were transfected with wildtype PAK4 or PAK4.S99A mutant as indicated. Samples were subjected to immunofluorescence analysis in which PAK4 was detected by using α-FLAG antibody and Alexa Fluor 488 as secondary antibody and endogenous pS3-cofilin by using α-pS3-cofilin antibody and Alexa Fluor 546 as secondary antibody. E. Free barbed end-induced actin incorporation at the leading edge is blocked when PAK4 is overexpressed, but not when PAK4.S99A is overexpressed. HeLa cells (5 × 104 cells, 8 well ibiTreat μ-slide) were transfected as indicated. To analyze cofilin-mediated actin incorporation F-actin free barbed ends were performed as described in materials and methods. PAK4-expressing cells were stained by immunofluorescence using primary antibodies directed against their tag as well as Alexa Fluor 488 as secondary antibody. Bar is 20 μm.