Figure 1. Cytoplasmic localization of anti-NeuN staining in a patient with HIV-associated asymptomatic cognitive impairment (ANI) (Paraffin sections).
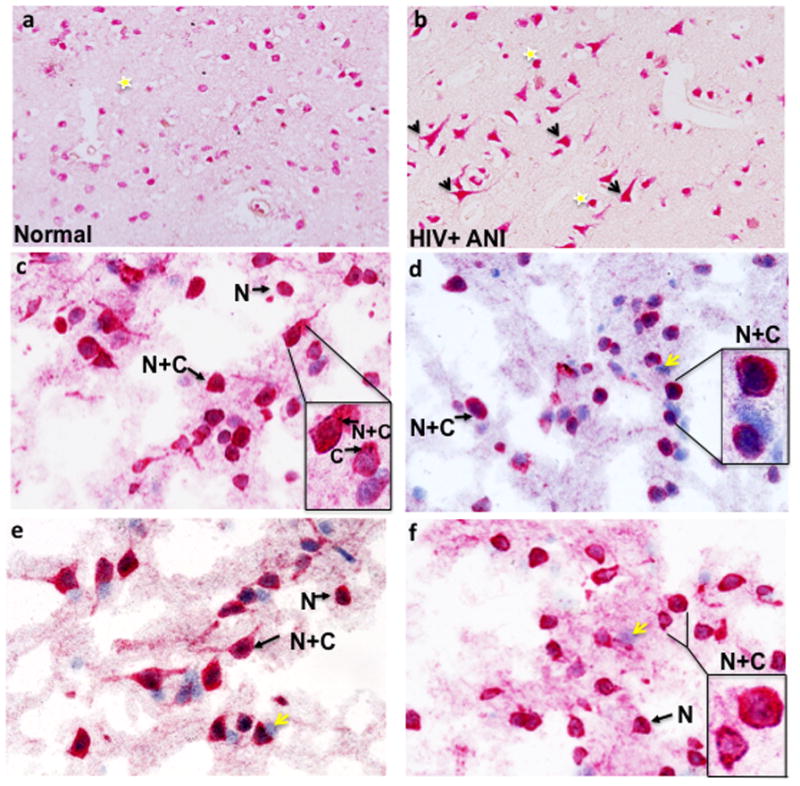
Yellow stars indicate nuclear localization and arrows highlight neurons with NeuN positivity in the cell body and axon. (a) Case number 14 with normal cognition and (b) case number 20, HIV+ ANI (see Table 1). NeuN immunoreactivity in four different normal controls (Frozen sections). Arrows highlight neurons with either nuclear exclusive staining (N) or nuclear and cytoplasmic reactivity (N+C). In the insets (Fig. 1c–f), cells are magnified to illustrate NeuN localization, including cytoplasmic exclusive staining. Yellow arrows indicate hematoxylin positive cells that do not react with anti-NeuN antisera. (a) case number 4, (b) case number 5, (c) case number 2 and (d) case number 1 (see Table 1).
