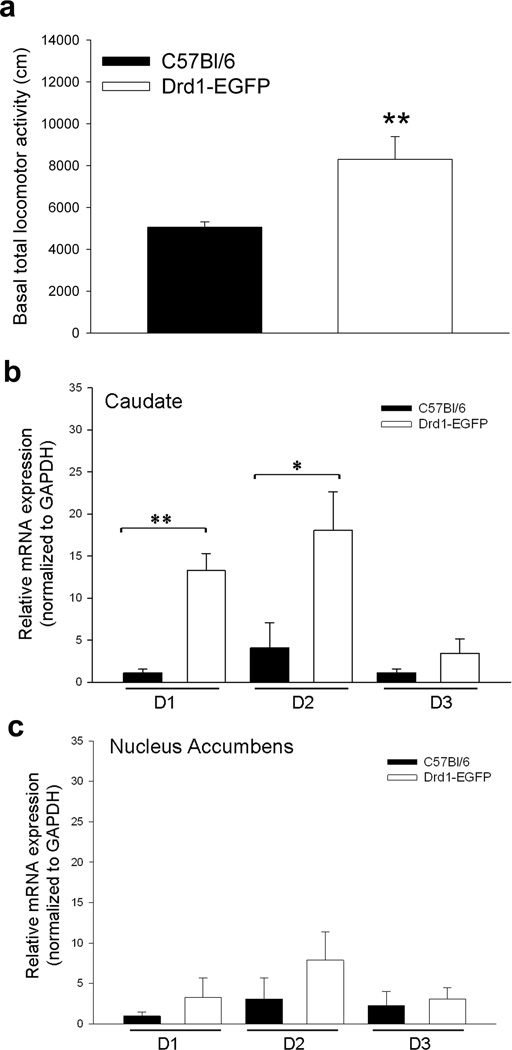
Figure 2.
Differences in basal locomotor activity and dopamine receptor expression between C57BL/6 and drd1-EGFP mice strains. (a) Total distance traveled (cm) during the initial 30 min after preadolescent (P30) C57BL/6 (black bar, n=12) and drd1-EGFP (white bar, n=8) mice are placed in the locomotor arena. The drd1-EGFP exhibited significantly greater locomotor activity (**, p<0.0.5, Student’s t-test). Error bars represent ± SEM. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR results of basal D1, D2, and D3 dopamine receptor mRNA levels normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels in caudate putamen (b) and nucleus accumbens (c) of C57BL/6 (black bars, n=4) and drd1-EGFP (white bars, n=4) preadolescent (P30) mice. Error bars represent ± SEM. The drd1-EGFP mice express significantly higher levels of D1 (**p< 0.001) and D2 (*p<0.05) receptor mRNA than the C57BL/6 mice in the caudate putamen (Student’s t-test).