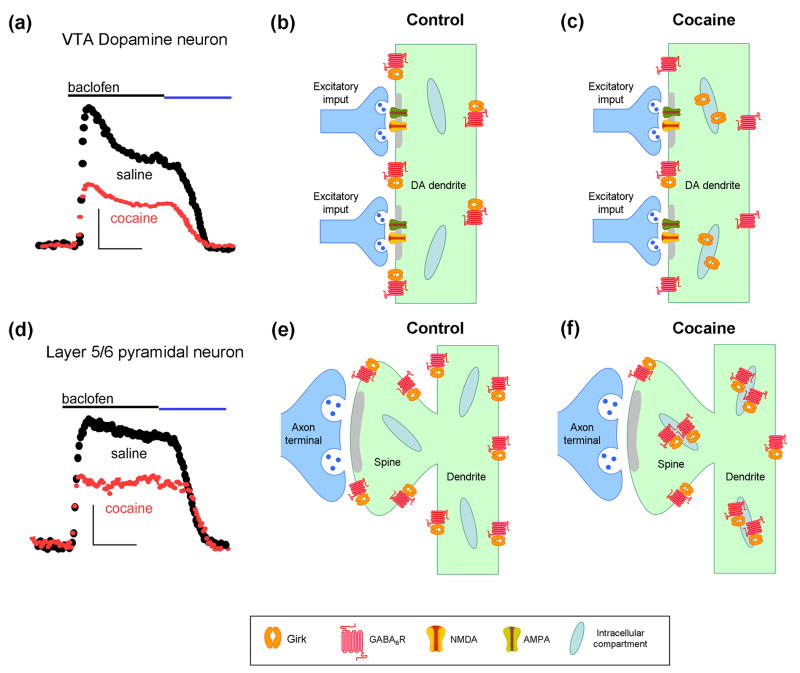
Figure 3. Plasticity of neuronal Girk signaling.
Cocaine-induced suppression of Girk signaling in VTA (a–c) and mPFC (d–f). a) A single cocaine injection reduced baclofen-induced (GABAB receptor-dependent) Girk currents in VTA dopamine neurons, an adaptation that persisted for up to 5 days, required activation of D2 dopamine receptors, and correlated with a redistribution of Girk2-containing channels (but not GABABR) from the cell surface to intracellular sites (b,c) [53]. (d) Repeated cocaine administration suppressed baclofen-induced Girk currents in Layer 5/6 pyramidal neurons, an adaptation that persisted for more than a month, required activation of D1 dopamine receptors, and correlated with a phosphorylation-dependent redistribution of Girk2-containing channels and GABAB receptors from the cell surface to intracellular sites (e,f) [55]. Blue line in the current traces shows that the baclofen-induced current was reversed by a GABAB receptor antagonist.