Figure 2.
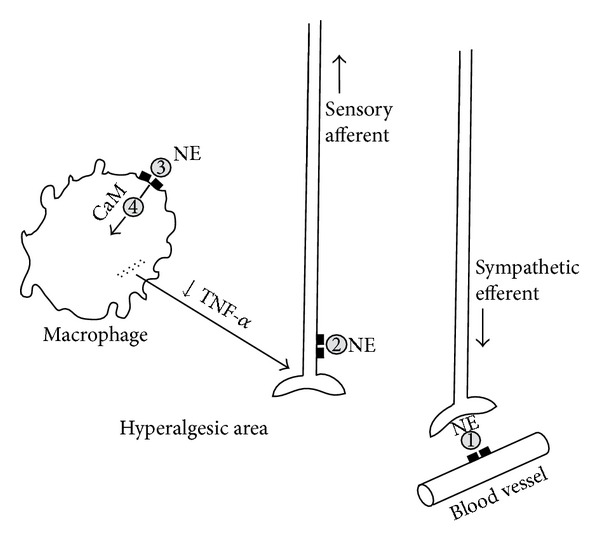
Depiction of possible sites of action of phenoxybenzamine in the suppression of neuropathic pain. Site 1) Blockade of norepinephrine (NE) effects on α 1-adrenergic receptors on blood vessels, thereby promoting vasodilation; Site 2) blockade of adrenergic receptors that populate afferent sensory fibers; Site 3) blockade of α 2-adrenergic receptors on the surface of macrophages, which appear to mediate release of proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α); Site 4) inhibition of calmodulin (CaM), which is involved in the cytokine-release process. (Schematically based on Figure 4 of Jänig and Baron, 2003; [23] reproduced with permission from Pain Practice, 2008 [19]).
