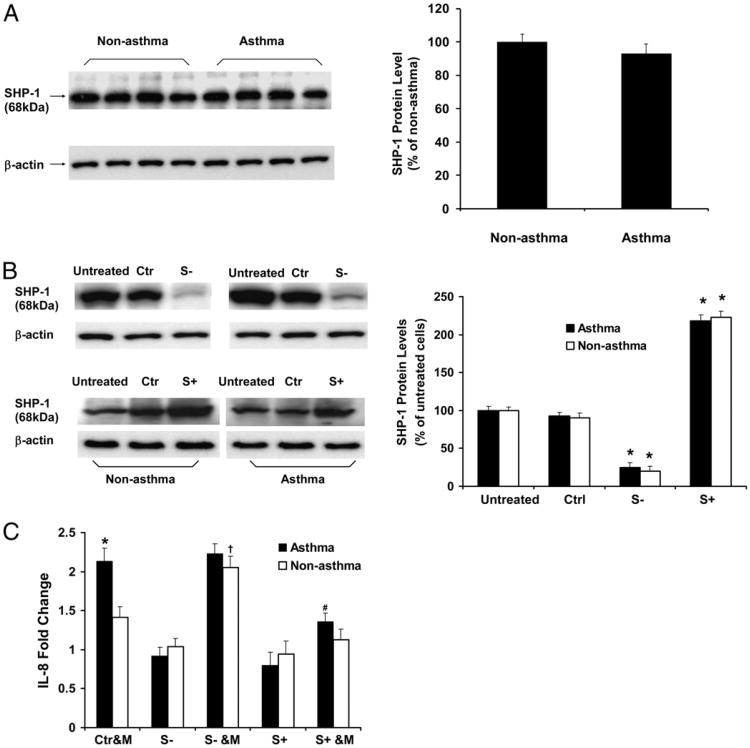
Figure 2.
IL-8 production in nonasthmatic and asthmatic airway epithelial cells infected with M. pneumoniae in the setting of SHP-1 knockdown and overexpression. (A) Immunoblot analysis of baseline SHP-1 expression in airway epithelial cells from nonasthmatic and asthmatic subjects. The data representing the percentage of densitometry values of nonasthmatic cells are expressed as mean ± SEM (right panel). (B) Immunoblot analysis of SHP-1 expression in airway epithelial cells without treatment (untreated), transduced with control rAAV only (Ctr), transduced with SHP-1–specific siRNA carrying rAAV to induce SHP-1 knockdown (S−), and infected with full-length SHP-1 cDNA carrying rAAV to induce SHP-1 overexpression (S+). The data representing the percentage of densitometry values of untreated cells are expressed as mean ± SEM (right panel). *p < 0.01 compared with untreated and control (Ctrl) in the same group. (C) Measurement of IL-8 production induced by M. pneumoniae in nonasthmatic and asthmatic airway epithelial cells with or without SHP-1 knockdown and overexpression. Data representing the fold change of IL-8 from control rAAV-transduced cells from the same group without mycoplasma infection are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 10 for nonasthma; n = 12 for asthma). Baseline SHP-1 expression was not different between asthmatic and nonasthmatic cells, and SHP-1 was knocked down and overexpressed similarly in nonasthmatic and asthmatic cells. IL-8 levels were higher in asthmatic cells infected with M. pneumoniae. SHP-1 overexpression reduced IL-8 production in asthmatic epithelial cells following mycoplasma infection. In the setting of SHP-1 knockdown, mycoplasma infection augmented IL-8 production in nonasthmatic, but not in asthmatic, cells.*,†p < 0.01 compared with Ctr&M of nonasthmatic cells; #p < 0.01 compared with Ctr&M or S− &M of asthmatic cells. Ctr&M, control rAAV-transduced airway epithelial cells treated with M. pneumoniae; S−, airway epithelial cells transduced with SHP-1–specific siRNA carrying rAAV to induce SHP-1 knockdown; S+, airway epithelial cells transduced with full-length SHP-1 cDNA carrying rAAV to induce SHP-1 overexpression; S− &M, airway epithelial cells with SHP-1 knocked down and infected by M. pneumoniae; S+ &M, airway epithelial cells with SHP-1 overexpressed and infected by M. pneumoniae.