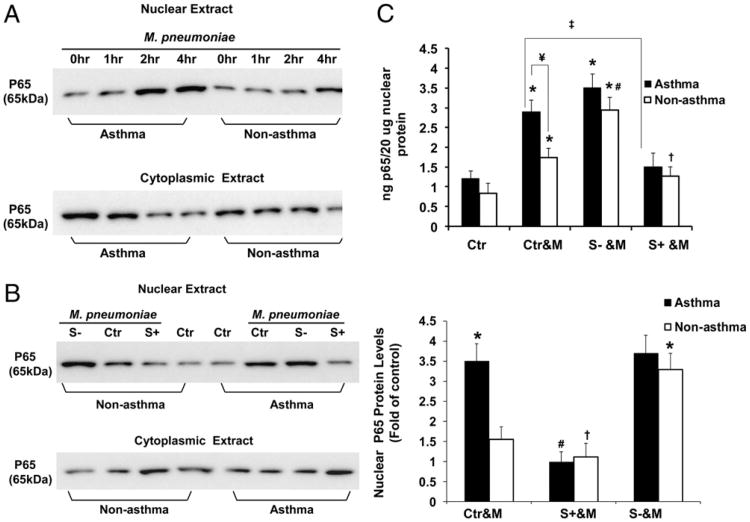
Figure 6.
NF-κB activation by M. pneumoniae and inhibition by SHP-1 in airway epithelial cells from nonasthmatic and asthmatic subjects. (A) Immunoblot of cytoplasmic and nuclear protein lysates against p65 in nonasthmatic and asthmatic airway epithelial cells without mycoplasma infection (0 h) or challenged with mycoplasma for 1, 2, or 4 h. (B) Immunoblot of cytoplasmic and nuclear protein lysates against p65 in nonasthmatic and asthmatic airway epithelial cells with or without SHP-1 knockdown or overexpression and infected with mycoplasma for 2 h (left panel). The amount of nuclear p65 NF-κB at 2 h after M. pneumoniae infection is expressed as fold change of densitometry values from cells in the same group transduced with control rAAV only (right panel). *p < 0.01, compared with Ctr&M of nonasthmatic cells; #p < 0.01, †p < 0.05, compared with Ctr&M in the same group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5). (C) NF-κB activation was quantified in nonasthmatic and asthmatic airway epithelial cells, with or without SHP-1 knockdown or overexpression, 2 h after mycoplasma infection. The NF-κB DNA-binding activity is reported as nanograms of bound p65 protein/20 μg of nuclear extracts. *p < 0.01, compared with Ctr in the same group; #p < 0.01, S− &M versus Ctr&M of nonasthmatic cells; †p < 0.05, S+ &M versus Ctr&M of nonasthmatic cells; ‡p < 0.01, S+ &M versus Ctr&M of asthma; ¥p < 0.01, nonasthma versus asthma. Data are presented as mean ± SEM values (n = 10 for nonasthma; n = 12 for asthma). Mycoplasma induced NF-κB activation in asthmatic cells, which was significantly higher than that in nonasthmatic cells and was attenuated by SHP-1 overexpression. SHP-1 knockdown dramatically increased NF-κB activation in nonasthmatic cells but not in asthmatic cells. Ctr, control rAAV-transduced airway epithelial cells; Ctr&M, control rAAV-transduced cells with mycoplasma treatment; S−, airway epithelial cells with SHP-1 knockdown; S+, airway epithelial cells with SHP-1 overexpression; S− &M, airway epithelial cells with SHP-1 knocked down and infected by M. pneumoniae; S+ &M, airway epithelial cells with SHP-1 overexpressed and infected by M. pneumoniae.