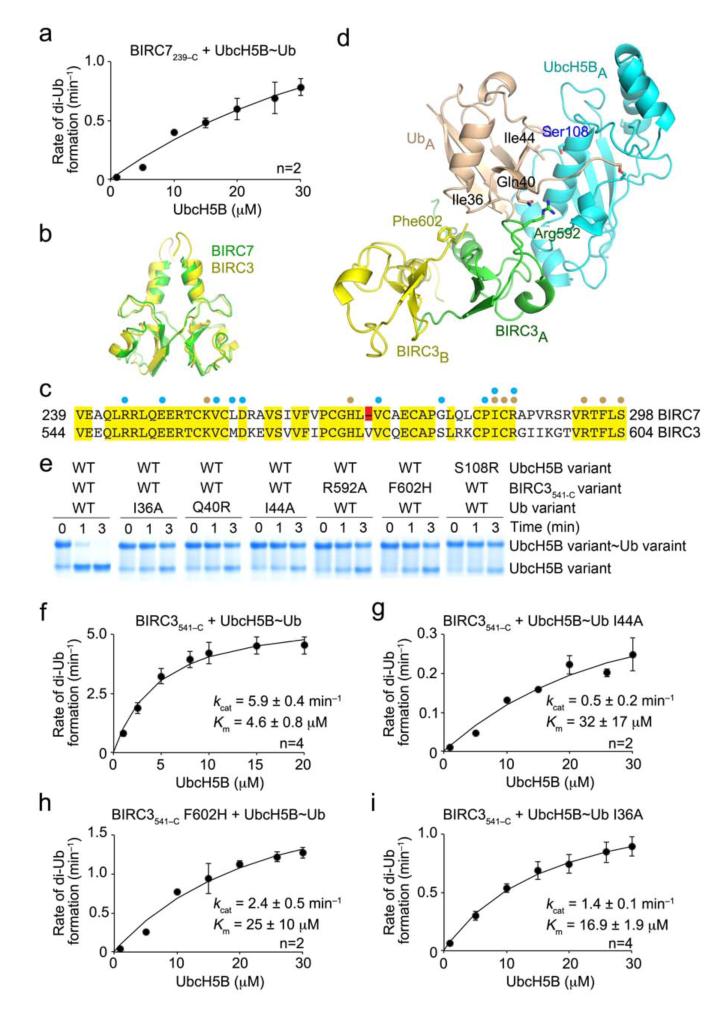
Figure 5.
Effect of donor Ub interactions on the kinetics of Ub transfer. (a) Single turnover kinetics of di-Ub formation catalyzed by BIRC7239–C. The rate of di-Ub formation was plotted against UbcH5B concentration. (b) Superposition of the structure of BIRC3541–C dimer (yellow, PDB 3EB6)17 onto BIRC7239–C dimer (green) from BIRC7239–C–UbcH5BRAS~Ub. BIRC3541–C dimer was generated from a symmetry-related molecule. (c) ClustalW sequence alignment of BIRC7 and BIRC3 RING domains. Identical residues are highlighted in yellow and the Val deletion in BIRC7 in red. Cyan and wheat circles indicate residues involved in contacting UbcH5B and Ub, respectively, as observed in BIRC7239–C–UbcH5BRAS~Ub and PDB 3EB6. (d) Models of UbcH5B~Ub bound to BIRC3541–C dimer generated by superposing BIRC3541–C dimer onto BIRC7239–C–UbcH5BRAS~Ub. Key residues involved in donor Ub interactions are indicated. Coloring is as described in Figs. 1 and 2. (e) Non-reduced SDS-PAGE of pulse-chase lysine discharge reactions showing the disappearance of UbcH5B~Ub with variants of BIRC3541–C, UbcH5B or Ub over time. (f–i) As in a but performed with BIRC3541–C. The rate of di-Ub formation was plotted against UbcH5B concentration for WT reaction (f), 32P-Ub I44A (g), BIRC3541–C F602H (h) and 32P-Ub I36A (i). Kinetic parameters and number of replicates, n, are indicated. Error bars indicate standard errors.