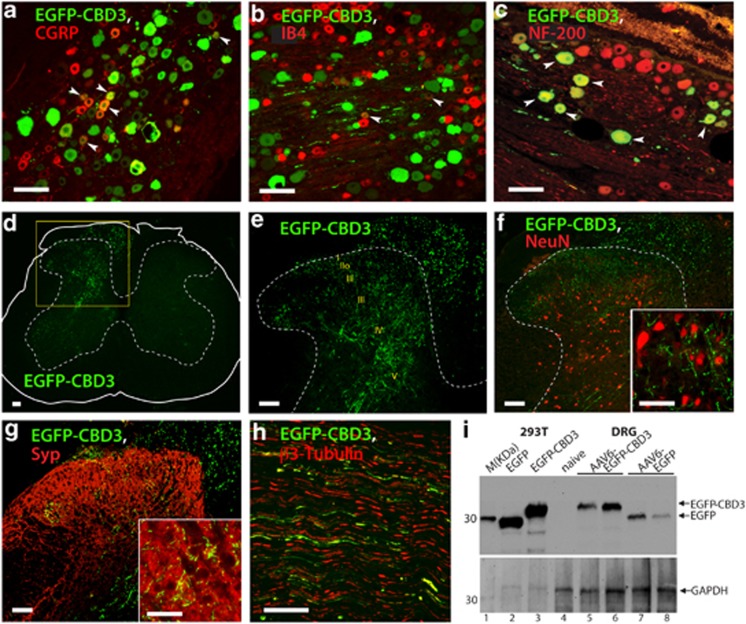
Figure 1.
Expression of fluorescent CBD3 in sensory neurons. DRG sections from rats in which AAV6-EGFP-CBD3 was injected 6 weeks previously and SNI traumatic nerve injury was performed 2 weeks thereafter were immunostained with antibodies to EGFP as well as CGRP (a), IB4 (b) or NF-200 (c). Arrowheads point to examples of co-labeled neurons. Spinal cord sections show EGFP-CBD3 expression (d, highlighted area magnified in (e) with enumerated laminae). No colocalization is observed with NeuN staining of dorsal horn neuronal somata (f, magnified in the inset, showing synaptic varicosities of transduced fibers). Sensory neuron fibers in the dorsal horn show cluster with the synaptic marker synaptophysin (g, magnified in the inset). The EGFP-CBD3 signal was also observed in sciatic nerve (h). Scale bars: 100 μm for all images except 50 μm for inset images. Western analysis (i) of HEK293T cell lysates following plasmid transfection show EGFP immunoreactivity at distinct molecular weights (MWs) for expressed EGFP (lane 2) versus EGFP-CBD3 (lane 3) as positive controls. DRG homogenates show no immunoreactivity in DRGs contralateral from the injection (lane 4), and appropriate MW in homogenates from DRGs injected with AAV6-EGFP-CBD3 (lanes 5 and 6) or AAV6-EGFP (lanes 7 and 8). Lane 1 shows marker protein standards (M; MagicMark, Life Technologies). Arrows point to the expected size bands for EGFP-CBD3 and EGFP (top panel), and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH, bottom panel) as a loading control.