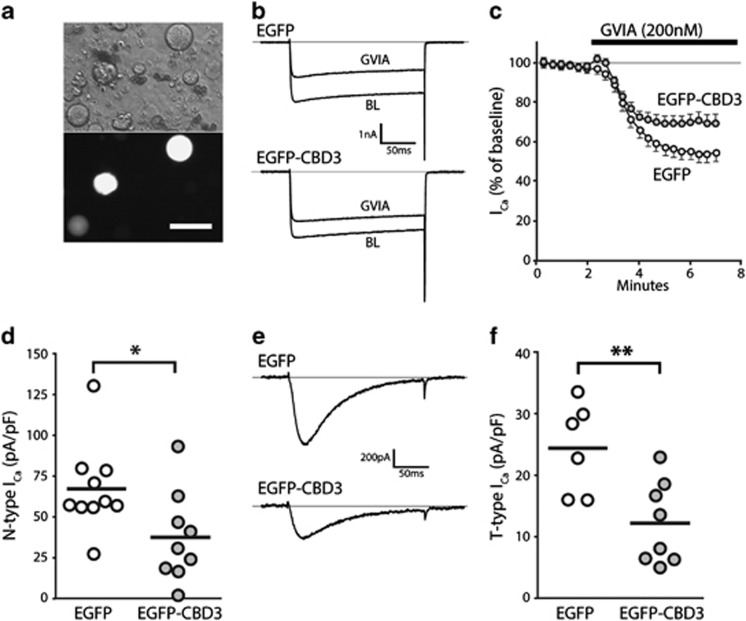
Figure 2.
Electrophysiological properties of neurons expressing EGFP-CBD3. Transduced neurons were identified after dissociation by EGFP epifluorescence (a, bottom image; top image: phase-contrast). N-type current was identified as the difference between current at baseline (BL) and after application of ω-Conotoxin-GVIA (GVIA, 200 nM) in response to depolarizations from −100 mV to VTest of 0 mV (b, sample traces; c, time course for group average) for neurons expressing EGFP (n=10) or EGFP-CBD3 (n=9). Summary data (d) show a significant depression of N-type current in neurons expressing EGFP-CBD3 compared with EGFP (*P<0.05). T-type current traces triggered by depolarizations from VH −100 mV to VTest of −30 mV (e) after incubation (20 min) with R-type current blocker SNX-482 (200 nM) and P/Q-type current blocker ω-Conotoxin MVIIC (200 nM), and addition of L-type current blocker nimodipine (5 μM) and GVIA (200 nM) to the recording bath. Summary data (f) show a significant depression of T-type current in neurons expressing EGFP-CBD3 compared with EGFP (**P<0.01).