Figure 1. Comparison of endogenous and virally-mediated exogenous Cx26 expression in the cochlea.
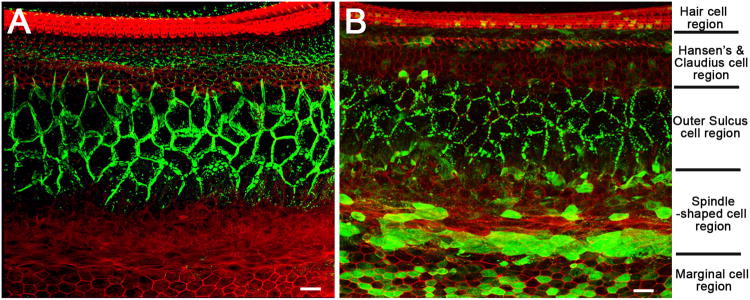
A) A confocal image showing the immunolabeling pattern of Cx26 (in green) taken from a flattened cochlear preparation of WT mouse. Major cochlear cell type regions are labeled on the right side of the figure. B) A confocal image showing the immunolabeling pattern of GFP (in green) taken from a flattened cochlear preparation of cCx26KO mouse received virus injection. The GFP is fused to the Cx26 in the design of the viral vector in order to differentiate exogenous Cx26 from residual endogenous Cx26 protein in the cCx26KO mice. The red counter-labeling was obtained with phalloidin conjugated to Alexa568. Scale bars in both panels represent approximately 20 μm.
