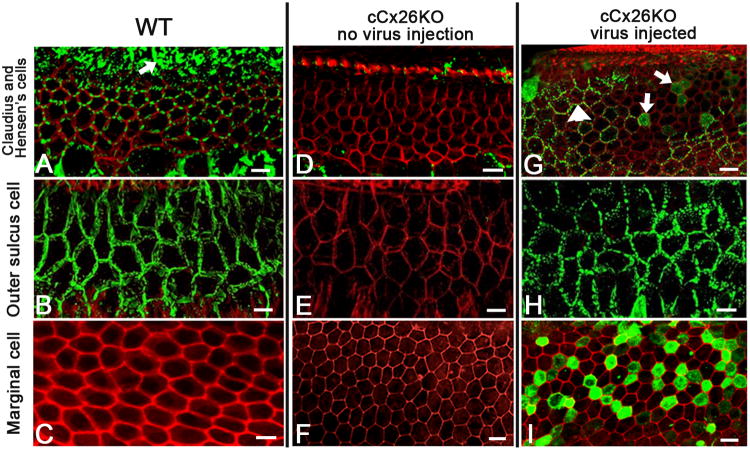
Figure 2. Detailed comparison of endogenous and virally-mediated exogenous Cx26 expression in cochlear cells.
A-C): Confocal images showing the immunolabeling patterns of Cx26 (in green) taken from a flattened cochlear preparation of WT mouse in the Claudius cells (cell membrane outlined by the hexagonal red phalloidin counterstaing) and Hensen's cells (an example is indicated by an arrow) (A), outer sulcus cell (B) and marginal cells (C).
D-F) Confocal images showing the immunolabeling patterns of Cx26 (in green) taken from a flattened cochlear preparation of untreated cCx26KO mouse in the cochlear regions of Claudius cells (D), outer sulcus cell (E) and marginal cells (F).
G-I) Confocal images showing the immunolabeling results (in green) with an antibody against the GFP, demonstrating the distribution patterns of Cx26-GFP fusion protein in the cochlea of treated cCx26KO mouse in the cochlear regions of Claudius cells (D), outer sulcus cell (E) and marginal cells (F). The red counter-labeling was obtained with phalloidin conjugated to Alexa568. Scale bars in all panels represent approximately 50 μm.