Figure 3.
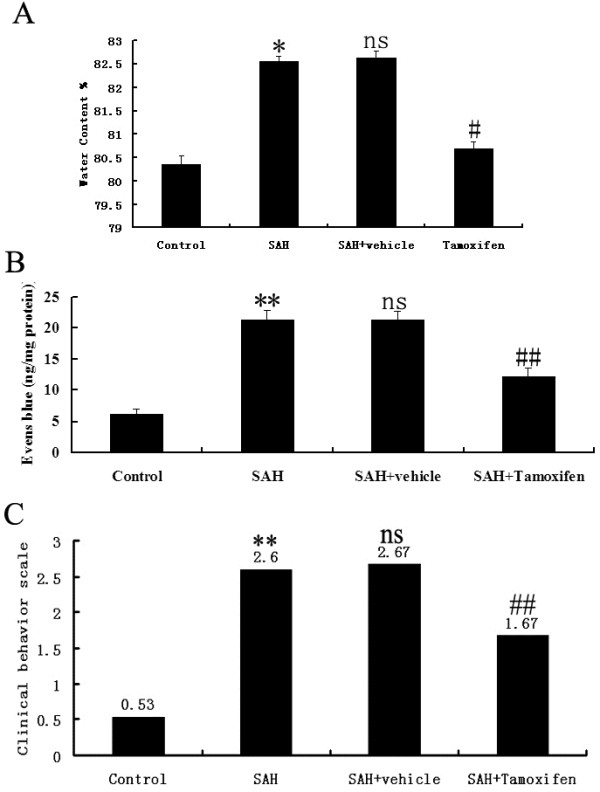
Alterations in brain water content in control group (n = 6), subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) group (n = 6), SAH + vehicle group (n = 6), and SAH + tamoxifen group (n = 6). (A) The brain water content was increased significantly at 48 h after SAH. Tamoxifen treatment markedly reduced brain water content. (B) Alterations in Evans blue extravasation in control group (n = 6), SAH group (n = 6), SAH + vehicle group (n = 6), and SAH + tamoxifen group (n = 6). SAH could induce a marked increase of blood-brain barrier (BBB) extravasation in the rat brain compared with control group. After tamoxifen administration, the Evans blue extravasation was significantly reduced as compared with SAH + vehicle group. (C) Effects of tamoxifen administration on functional outcomes in the control group (n = 18), SAH group (n = 18), SAH + vehicle group (n = 18), and SAH + tamoxifen group (n = 18). Compared to rats in SAH + vehicle group, Tamoxifen administration attenuated the SAH-induced impairment in the performance tested at 48 h after SAH. *P <0.05 and **P <0.01 between control animals versus SAH animals; #P <0.05 and ##P <0.01 between SAH + vehicle animals versus SAH + tamoxifen animals; n.s. P >0.05 between SAH animals versus SAH + vehicle animals.
