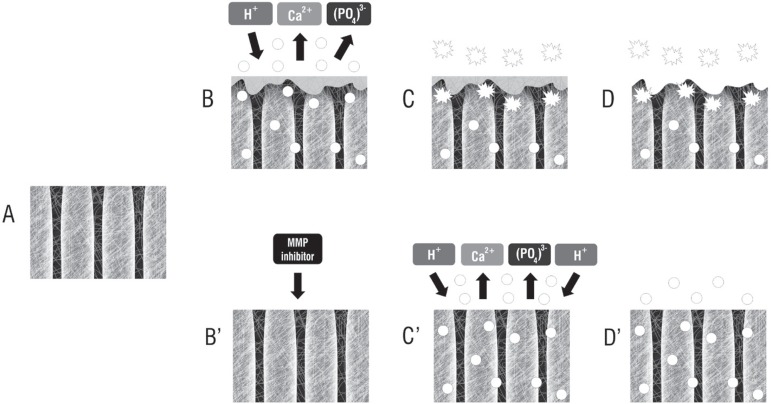
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanism of action of Matrix Metallloproteinases (MMPs) on dentin erosion. Spheres: inactive MMP. Asterisk shapes: active MMP. (A) Sound dentin. After the erosive challenge, the dentin surface is demineralized (B), causing the exposure of the collagen fibrils (C). When unprotected by a MMP inhibitor, the collagen fibrils are exposed by the action of the acid of the soft drink and the collagen fibrils hydrolysed (C, D). By the inhibition of dentin-bound and/or salivary MMPs (B’), the preserved organic layer prevents further demineralization during the subsequent erosive challenges (C’), resulting in a significant decrease in erosive wear (D’). Illustration modified from Kato, et al.52 (2010)