Fig. 4. Curcumin and sulforaphane inhibits TLR4 dimerization induced by LPS and sulforaphane binds to cysteines in TLR4 extracellular domain.
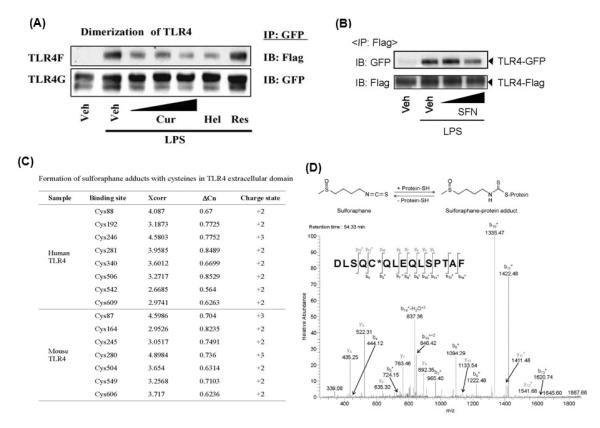
(A, B). Ba/F3 cells expressing TLR4-Flag (TLR4F), TLR4-GFP (TLR4G), MD2-Flag (MD2F), and CD14 were pre-treated with curcumin (10, 20, 50 μM), helenalin (5 μM), resveratrol (50 μM), or sulforaphane (10, 20 μM) for 1 h and then treated with LPS (50 ng/ml) for 20 min. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotted (IB) with antibody as indicated. (C) Summary of cysteines in human and mouse TLR4, which bind to sulforaphane. Extracellular domain of human TLR4 (a.a. 27-631) or mouse TLR4 (a.a. 26-629) was incubated with sulforaphane and micro LC-MS/MS analysis was performed. (D) (Upper panel) Schematic diagram of reaction of sulforaphane with protein cysteine residue. (Lower panel) MS/MS spectrum of the SFN-cysteine adducts at human TLR4 (Asp502-Phe516; DLSQC506QLEQLSPTAF). * denotes fragment ions with one SFN. Cur, curcumin; Hel, helenalin; and Res, resveratrol; SFN, sulforaphane. Reproduced with permission from Biochemical Pharmacology and Journal of Immunology.
