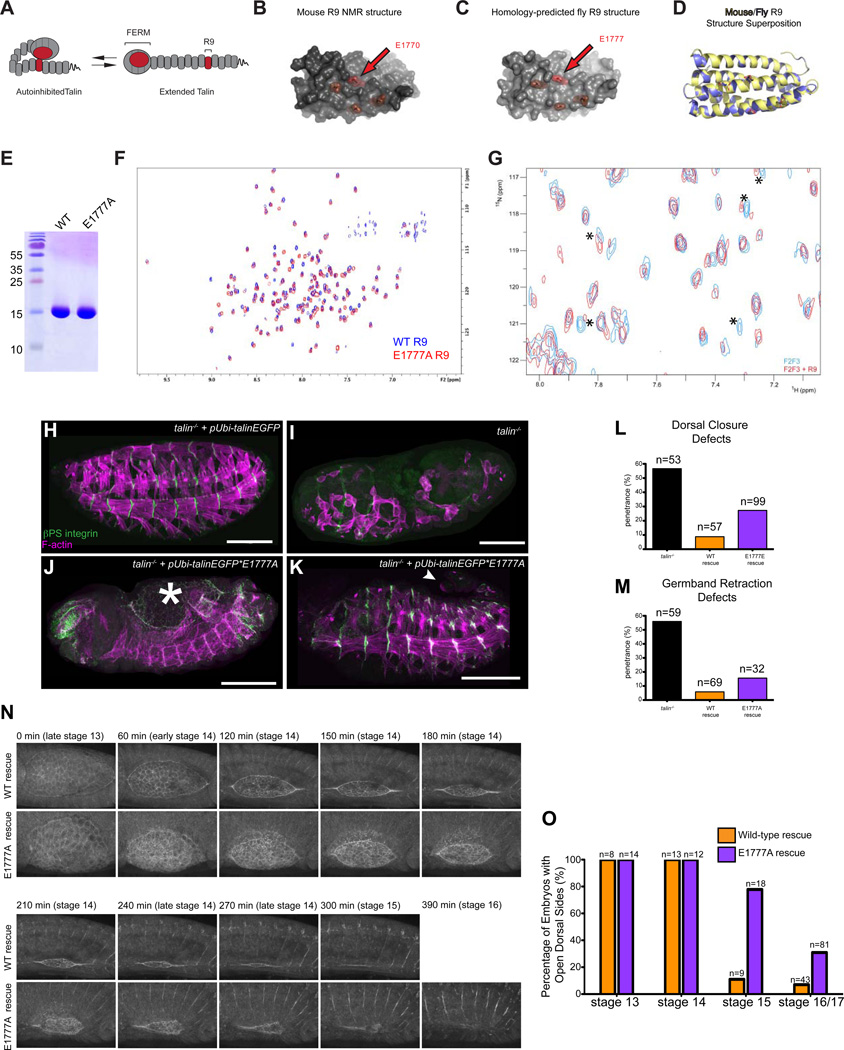
Figure 1. Disruption of a conserved autoinhibitory intramolecular interaction between the talin FERM and the talin rod leads to morphogenetic defects including delayed dorsal closure.
(A) Cartoon schematic of talin autoinhibition. (B-D) The NMR structure[5] of mouse R9 (B) and our homology-predicted model of fly talin R9 (C). Critical residues for F3-rod binding are highlighted in red. (D) Superposition of the mouse NMR structure (yellow) and the homology-modeled fly structure (blue). (E) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing that purified recombinant WT and E1777A fly R9 domains exhibit similar electrophoretic mobility at the expected molecular weight. (F) 1H,15N-TROSY-HSQC spectra of 150 µM 15N-labeled WT talin R9 (blue) and R9 E1777A (red). The R9 E1777A mutant shows a well dispersed NMR spectrum similar to that of the wildtype R9 indicating that the mutation does not affect the tertiary structure of the domain. (G) A 1H,15N-TROSY-HSQC spectra of 25 µM 15N-labeled fly talin F2F3 alone (blue) or in the presence of the talin rod R9 domain (red). In the presence of R9, some of the peaks have shifted and broadened (indicated by asterisks) compared to the spectra of the free F2F3 providing evidence of a direct interaction between fly F2F3 and R9. (H-M) Late stage talin-null embryos stained for integrin (green in H-K) and F-actin (magenta in H-K) were scored for phenotypes in the morphogenetic processes DC (J,L; asterisk in J demarcates open dorsal hole) and GBR (K,M; arrowhead in K shows un-retracted tail). Embryos were rescued with talinEGFP (H) construct or the talinEGFP*E1777A autoinhibition mutant construct (J-K). (N-O). Talin-null embryos rescued with either talinGFP or talinEGFP*E1777A were scored for dorsal holes at stage 13–17 (see Experimental Procedures). (O) Images from time-lapse movies of WT-rescued embryos (top) or E1777A mutant (bottom) embryos expressing talinGFP*E1777A and undergoing DC at the indicated time-points.