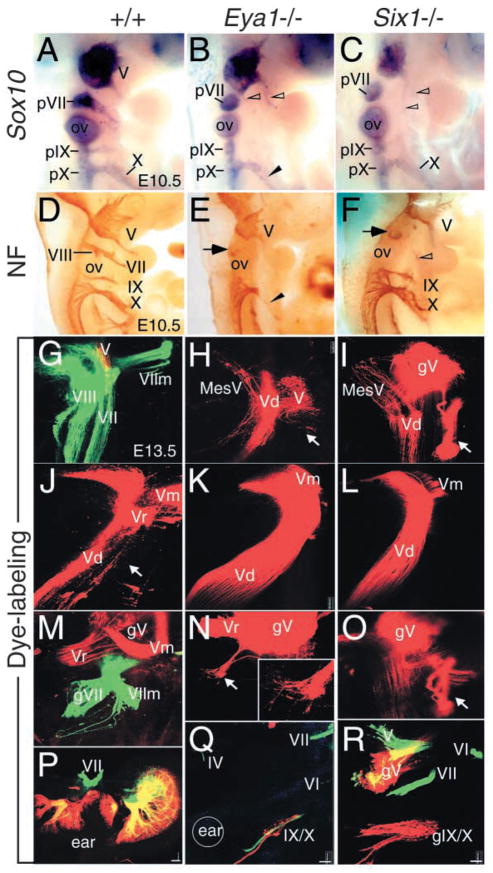
Fig. 6.
Eya1 and Six1 regulate the patterning of cranial sensory nerves and their associated ganglia. (A–C) E10.5 whole-mount embryos hybridized with a Sox10 riboprobe. The proximal VIIth (pVII), IXth (pIX) and Xth (pX) ganglia are present in Eya1−/−(B) or Six1−/− (C) embryos. Truncated distal Xth ganglion (X) is present in Eya1−/− embryos (arrowhead, B). (D–F) E10.5 whole-mount embryos immunostained with an antibody against Neurofilament (NF). The VIIIth and distal VIIth, IXth and Xth ganglia are apparent in wild type embryos (D). However, the VIIIth and the distal VIIth ganglia are missing in Eya1−/− (E) and Six1−/− (F) embryos. While the distal IXth is completely absent but the distal Xth ganglion is truncated in Eya1−/− (arrowhead, E), both are present in Six1−/− embryos (F). Arrow points to the proximal VIIth ganglion in the mutants (E,F). Nerves originating from the Vth ganglion sometime innervate the second branchial arches in both mutants (open arrowheads). (G–R) Whole-mount images of E13.5 wild-type (G,J,M,P), Eya1−/− (H,K,N,Q) and Six1−/− (I,L,O,R) embryos show the development of cranial nerves using lipophilic dyes to trace the fibers from the nerves into the brain (G–O) and from the brain to the periphery (P–R). (G) An image shows the VIII projection (left two layers; vestibular and cochlear projection), the V/VII projection (green), the VII motor root (VIIm, green) and partial V projection (red) in normal animals. (H) There is no VIII nerve projection in any E13.5 Eya1−/− or (I) Six1−/− animals after applications to the hyoid (VII nerve) arch. However, the VII motoneurons were filled from the V nerve in both mutants (arrow). In addition, a V sensory component (MesV) projects not into the descending V (Vd) tract but rather into the area that receives the inner ear projection in normal animals. (J) A whole-mount image shows the V descending tract (Vd), V root (Vr) and motoneurons (Vm) in E13.5 normal animals. (K,L) Images show obvious expansion of the V projection in Eya1−/− (K) and Six1−/− (L) embryos. (M) V (red) and VII (green) ganglia and roots are shown as they approach the brain. (N) There is small projection of VII fibers out of the V ganglion in Eya1−/− animals (arrow). (O) In Six1−/− embryos, some VII motoneurons reroute directly into the V ganglion (gV) (arrow) or project outside the brain only to join the V nerve (compare images of I and O, which are taken form a lateral and a medial perspective of the same brain). (P) A motoneuron injection (green) and a sensory alar plate injection (red) caudal to the ear labels the VIII and VII nerves around the ear. (Q) In Eya1−/− embryos, only a few sensory neurons of the IX/X ganglia (red), abducens (VI), V and trochlear (IV) nerves (all green) are labeled. Circle indicates the approximate position of the ear. (R) In this Six1−/− animal, the VII motoneurons exit separately from V but join the V fibers outside the brain. Note the more profound reduction in IX/X ganglion size in Eya1 mutants (Q,R). Anterior is up and dorsal is to the left in all images. Scale bar: 100 μm.