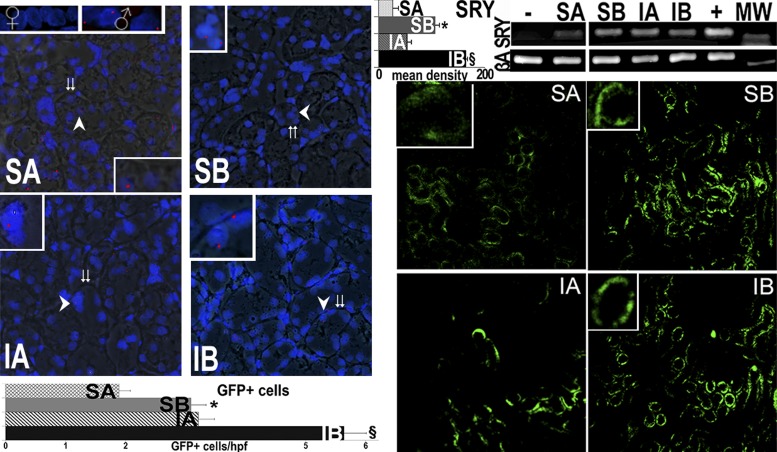
Fig. 5.
Male tubular cell engraftment in female kidneys. Engraftment of infused cells is shown via fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH; red) for the Y chromosome. Merged fluorescence and bright images show FISH-positive cells from male donors in tubules of female kidneys 14 wk after the final cytotherapy treatment (age: 34 wk) as well as in normal males but not in female kidneys (insets show the areas at the arrows). Double arrows show tubular basement membranes. In addition, specific DNA encoding the male determinant gene sex-determining region on the Y chromosome (SRY) was found in female kidneys that received male tubular cells but not in female kidneys that did not receive cells (negative control). The positive controls correspond to DNA extracted from the normal liver of male Sprague-Dawley rats. Mean band density for the SRY PCR is presented in top graph. Right: GFP-positive cells within kidneys of rats treated with control (A) or SAA-positive (B) cells with quantification of GFP-positive cells in a total of 212 high-power fields (hpf). In contrast, GFP-positive cells were <1 cells/hpf in kidneys of normal rats without renal injury (16). GFP-positive cells were very rarely seen in other organs (Table 2). MW, molecular weight marker; βA, β-actin (to insure the equivalent DNA substrate for PCR). *P < 0.05 vs. SA; §P < 0.05 vs. IA.