Figure 5.
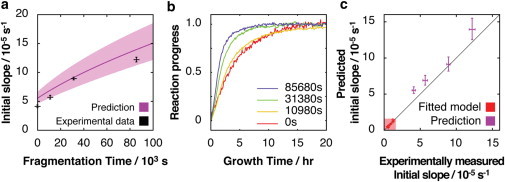
Prediction of the ability of a fibril sample to seed as fibril fragmentation proceeds. (a) Predicted (purple line) and measured (black cross) seeding efficiency characterized by the initial slope of seeded fibril growth using the fibril sample as a function of fragmentation time. The error bars on the measured data points indicate one standard error from six replicate reactions. The shaded area indicates 95% confidence functional prediction bounds. (b) Typical fibril growth reaction progress curves of reactions seeded by fibril samples taken from the fragmentation reaction shown in Fig. 4, monitored by ThT fluorescence. All curves are normalized to their upper baselines. The time each sample was fragmented before addition to excess monomer to stimulate fibril growth are shown in the inset. (c) Predicted initial slopes of seeded fibril growth compared with the measured initial slopes. The red shaded area contains data points used to calculate the fibril elongation rate constant (the same as shown in Fig. 3 b) to indicate predictive power at extrapolated seeding conditions. The error bars indicate one standard error. To see this figure in color, go online.
