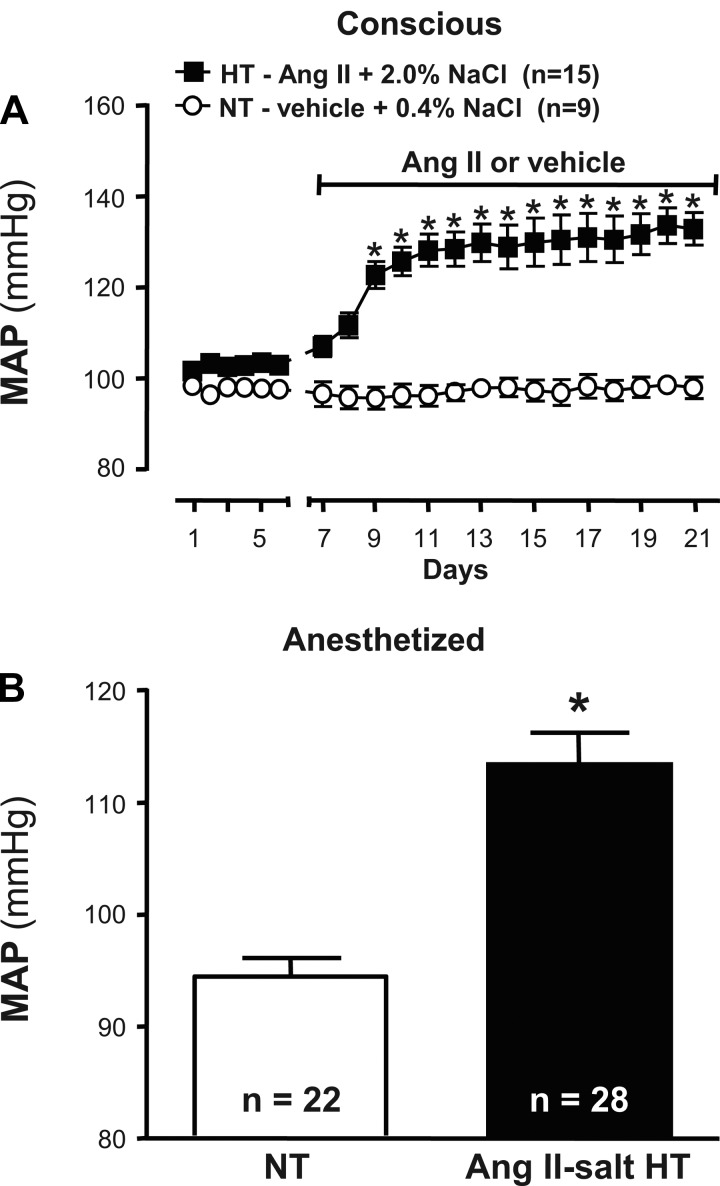
Fig. 1.
Effect of ANG II combined with a high-salt diet and sham treatment on mean arterial pressure (MAP) in conscious and anesthetized rats. A: baseline values of MAP were recorded by radio telemetry for 6 days before initiating 14 days of subcutaneous infusion of vehicle (normal saline; NT, ○) or ANG II (150 ng·kg−1·min−1; HT, ■). Values of MAP in NT and HT rats were similar at baseline (note that error bars are smaller than symbols). In vehicle-infused NT rats that consumed a normal salt (0.4% NaCl) diet, MAP values throughout the infusion period did not deviate significantly from baseline. In ANG II-infused HT rats that consumed a high-salt (2% NaCl) diet, MAP values increased during the first ∼5 days of treatment. Thereafter, MAP remained stably elevated such that values were significantly greater than sham-treated controls (*P < 0.001). B: during cell recording experiments, resting MAP under urethane/chloralose anesthesia remained significantly elevated in HT (black bar) compared with NT (white bar) rats (*P < 0.01).