Fig. 5.
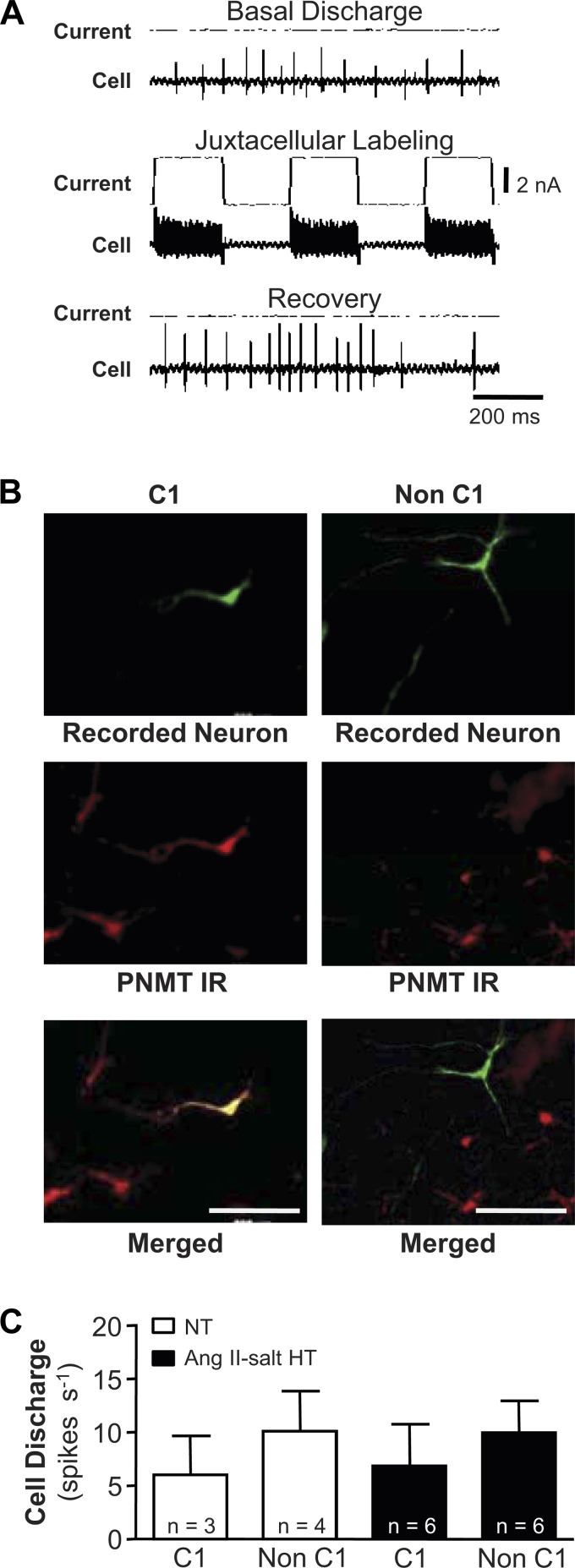
Neurochemical phenotyping of RVLM neurons. A: example traces illustrate the juxtacellular labeling technique. Discharge of a representative RVLM neuron is shown at rest (top traces), during delivery of positive current pulses through the recording electrode to entrain discharge (during which the recorded neuron is filled with biotinamide [middle traces]), and during recovery (bottom traces). B: histological processing of brain tissue was performed to recover recorded neurons that were successfully filled with biotinamide using the juxtacellularly labeling technique (at top; green). Immunohistochemical processing of the same tissue sections revealed the presence of the epinephrine synthetic enzyme phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase (PNMT), thereby marking the location of C1 cells (at middle; red). Merged images (bottom) reveal double-labeled neurons that belong to the C1 cell group (at left; yellow) and nondouble labeled neurons that do not (at right; green). C: summary data show that resting discharge frequencies were similar among C1 and non-C1 neurons from NT and HT rats. IR, immunoreactivity.