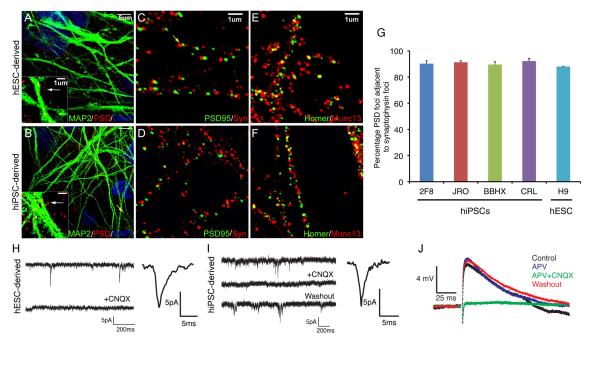
Figure 7. Formation of functional excitatory synapses among PSC-derived cortical projection neurons.
A-F. Super-resolution microscope images of dendrites (MAP2, green, A, B) showing localization of foci of the excitatory synapse-specific PSD95 protein (A-D). Physical synapses (arrows in all images) were identified by juxtaposition of pre- and post-synaptic protein complexes, either synaptophysin and PSD95 (C, D) or Munc13 and Homer (E, F). Scale bars as shown.
G. Quantification of the proportion of PSD-95 foci that were found juxtaposed to synaptophysin foci in cortical neuronal cultures derived from four hiPSC and one hESC line. In all cases approximately 90% of PSD-95 foci were found colocalised with synaptophysin. Error bars, SD. See methods for technical details.
H, I. Detection of mEPSCs in whole cell recordings of hESC (H) or hiPSC (I)-derived cortical neurons. The AMPA receptor antagonist CNQX blocked the appearance of mEPSCs. Also shown are average mEPSC from hESC (n=20 events; H) and hiPSC (n=20 events; I) derived cortical neurons.
J. Evoked post-synaptic potentials (PSPs) in hESC and hiPSC-derived cortical neurons are excitatory (n=9 neurons) and blocked by the AMPA receptor antagonist CNQX (50 μM; n=4 neurons). Addition of the NMDA receptor antagonist APV (50 μM) had no detectable effect on evoked PSPs (n=2 neurons). Averaged recordings (Control, 7 trials; APV 13 trials; CNQX, 10 trials; Washout, 10 trials) from a representative neuron are shown.