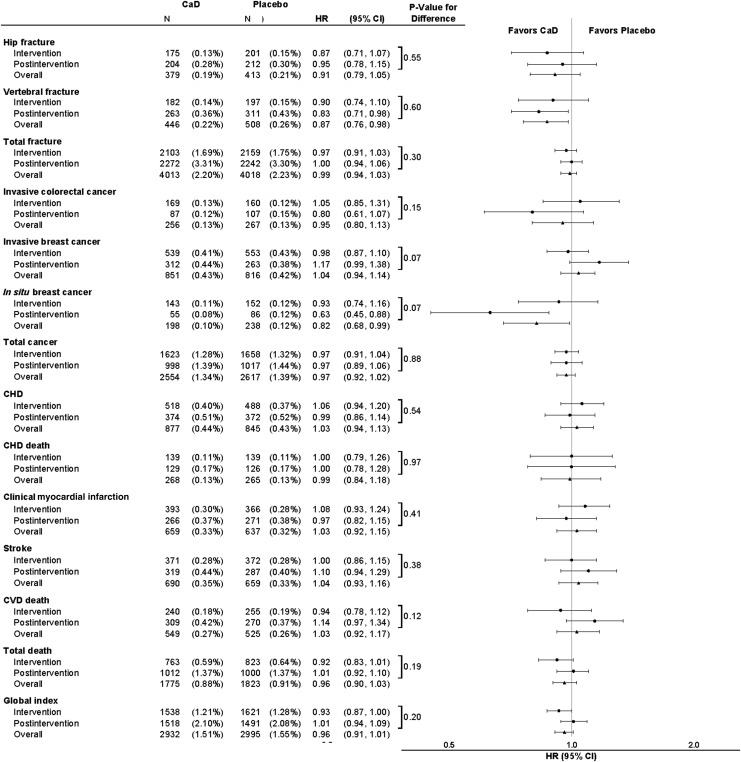
FIG. 1.
Incident clinical events by randomization assignment and corresponding hazard ratios (HRs) for the intervention, postintervention, and overall follow-up period. The HR and 95% confidence interval (CI) for intervention period events are derived from a proportional hazards model stratified on age, prevalent condition (where appropriate), and randomization arm in the hormone therapy (HT) and diet modification (DM) trials, where time to event equals 0 on date of randomization. The HR and CI for postintervention period events are derived from a Cox proportional hazards model stratified on age, prevalent condition (where appropriate), and randomization arm in the HT and DM trials, where time to event equals 0 on calcium and vitamin D (CaD) trial close-out date. The HR and CI for the overall combined period events are derived from a proportional hazards model stratified by prevalent condition (where appropriate), age, HT and DM randomization arm, and trial phase (time-dependent), where time to event equals 0 on date of randomization. P-values for the difference between the intervention and postintervention periods are derived from a Cox proportional hazards models stratified by prevalent condition (where appropriate), age, HT and DM randomization arm, and trial phase (time-dependent), where time to event equals 0 on date of randomization. The p-value tests whether the HR for the intervention period equals the HR for the postintervention period. All nonhip fractures use adjudicated data during the clinical trial and self-reported data thereafter.