Fig. 6.
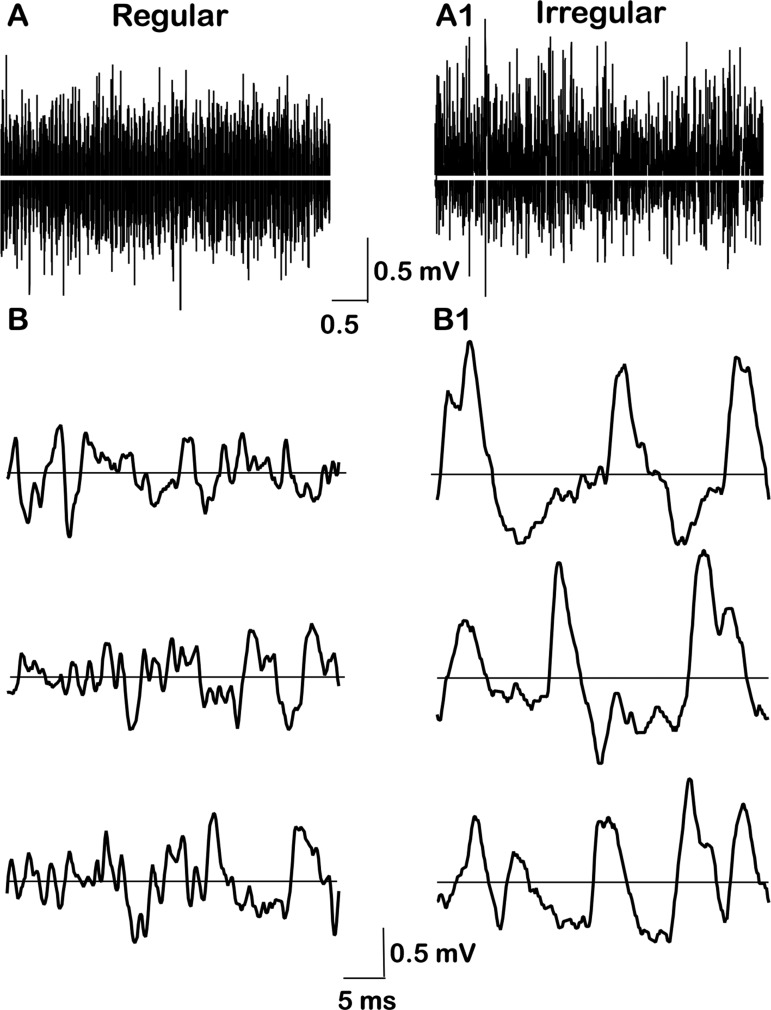
Shot-noise theory is used to estimate quantal rate (qrate) and quantal size (qsize). Voltage records of resting activity, 5 s duration, for the 2 exemplar units, one regular (A) and the other irregular (A1). Both records are high-pass filtered and spikes are removed. Horizontal (white) lines, 0 mV. Variances are similar for the 2 units: (0.0533 mV2, irregular unit; 0.0401 mV2, regular unit); third central moment (skew) is much larger in the irregular unit (7.85 × 10−3 mV3 vs. 2.87 × 10−4 mV3). From this combination of central moments, qsize is estimated to be larger and qrate smaller in the irregular unit. B: expanded time base for low-pass versions of the voltage records, 40-ms duration, 3 samples. Exemplar regular (B) and irregular (B1) units illustrating the higher qrate and smaller qsize for the regular unit. Calibrations: top for A and A1; bottom for B and B1.