Abstract
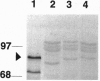
The R-sc gene of maize is a member of the R gene family of transcriptional activators that regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis. A derivative of R-sc, r-m9 conditions a reduced level of aleurone pigmentation due to the presence of a 2.1-kb Ds insertion near the 3' end of the coding region. Excision of Ds from r-m9 leaves a 7-bp insertion in the darker but still mutant v24 derivative. Both the 7-bp insertion in v24 and the 2.1-kb Ds in r-m9 are predicted to truncate their respective R proteins proximal to the carboxyl terminus, which was shown previously to contain one of three nuclear localization sequences. We find that the reduced expression of r-m9 and v24 are not due to mRNA or protein instability, but most likely reflect the inefficient localization of truncated R proteins to the nucleus. To our knowledge this is the first example of a transposable element insertion that alters gene expression by affecting nuclear localization. In addition, our data indicate that the carboxyl terminus of the R protein is far more important than previously suspected and illustrates the utility of natural mutations for defining functional domains in proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alleman M., Kermicle J. L. Somatic variegation and germinal mutability reflect the position of transposable element Dissociation within the maize R gene. Genetics. 1993 Sep;135(1):189–203. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft I., Dean C. Transposition pattern of the maize element Ds in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics. 1993 Aug;134(4):1221–1229. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.4.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodeau J. P., Walbot V. Regulated transcription of the maize Bronze-2 promoter in electroporated protoplasts requires the C1 and R gene products. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):379–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00265434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink R. A., Williams E. Mutable R-navajo alleles of cyclic origin in maize. Genetics. 1973 Feb;73(2):273–296. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consonni G., Viotti A., Dellaporta S. L., Tonelli C. cDNA nucleotide sequence of Sn, a regulatory gene in maize. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):373–373. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Keller J., Harper E., Ralston E. Variable Patterns of Transposition of the Maize Element Activator in Tobacco. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):473–482. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Mauvais J., Chaleff D. Molecular studies on mutations at the Shrunken locus in maize caused by the controlling element Ds. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):11–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroux M. J., Clancy M., Baier J., Ingham L., McCarty D., Hannah L. C. De novo synthesis of an intron by the maize transposable element Dissociation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12150–12154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Cone K. C., Chandler V. L. Functional analysis of the transcriptional activator encoded by the maize B gene: evidence for a direct functional interaction between two classes of regulatory proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):864–875. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Klein T. M., Roth B. A., Fromm M. E., Cone K. C., Radicella J. P., Chandler V. L. Transactivation of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes following transfer of B regulatory genes into maize tissues. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2517–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J., Anderson B., Wessler S. R. Isolation and characterization of rice R genes: evidence for distinct evolutionary paths in rice and maize. Genetics. 1996 Mar;142(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1093/genetics/142.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermicle J. L. Probing the component structure of a maize gene with transposable elements. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1457–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4451.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig S. R., Habera L. F., Dellaporta S. L., Wessler S. R. Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7092–7096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M. A., Chen J., Greenblatt I., Dellaporta S. L. Reconstitutional mutagenesis of the maize P gene by short-range Ac transpositions. Genetics. 1992 Aug;131(4):939–956. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.4.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly C., Shepherd N. S., Pereira A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Bertram I., Robertson D. S., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Molecular cloning of the a1 locus of Zea mays using the transposable elements En and Mu1. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):877–882. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. I., Baker B. Movers and shakers: maize transposons as tools for analyzing other plant genomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;7(3):406–413. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purugganan M. D., Wessler S. R. Molecular evolution of the plant R regulatory gene family. Genetics. 1994 Nov;138(3):849–854. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabino I., Mancinelli A. L. Light, temperature, and anthocyanin production. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):922–924. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radicella J. P., Brown D., Tolar L. A., Chandler V. L. Allelic diversity of the maize B regulatory gene: different leader and promoter sequences of two B alleles determine distinct tissue specificities of anthocyanin production. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2152–2164. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens C. M., Munyikwa T. R., Overduin B., Nijkamp H. J., Hille J. Transposition pattern of a modified Ds element in tomato. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;21(6):1109–1119. doi: 10.1007/BF00023607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth B. A., Goff S. A., Klein T. M., Fromm M. E. C1- and R-dependent expression of the maize Bz1 gene requires sequences with homology to mammalian myb and myc binding sites. Plant Cell. 1991 Mar;3(3):317–325. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.3.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefelbein J. W., Furtek D. B., Dooner H. K., Nelson O. E., Jr Two mutations in a maize bronze-1 allele caused by transposable elements of the Ac-Ds family alter the quantity and quality of the gene product. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):767–777. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott L., LaFoe D., Weil C. F. Adjacent sequences influence DNA repair accompanying transposon excision in maize. Genetics. 1996 Jan;142(1):237–246. doi: 10.1093/genetics/142.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Genes encoding actin in higher plants: intron positions are highly conserved but the coding sequences are not. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):111–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh M. W., Wessler S. R., Raikhel N. V. Nuclear targeting of the maize R protein requires two nuclear localization sequences. Plant Physiol. 1993 Feb;101(2):353–361. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varagona M. J., Schmidt R. J., Raikhel N. V. Monocot regulatory protein Opaque-2 is localized in the nucleus of maize endosperm and transformed tobacco plants. Plant Cell. 1991 Feb;3(2):105–113. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil C. F., Marillonnet S., Burr B., Wessler S. R. Changes in state of the Wx-m5 allele of maize are due to intragenic transposition of Ds. Genetics. 1992 Jan;130(1):175–185. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil C. F., Wessler S. R. Molecular evidence that chromosome breakage by Ds elements is caused by aberrant transposition. Plant Cell. 1993 May;5(5):515–522. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.5.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R., Baran G., Varagona M. The maize transposable element Ds is spliced from RNA. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):916–918. doi: 10.1126/science.3039661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
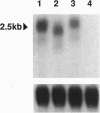
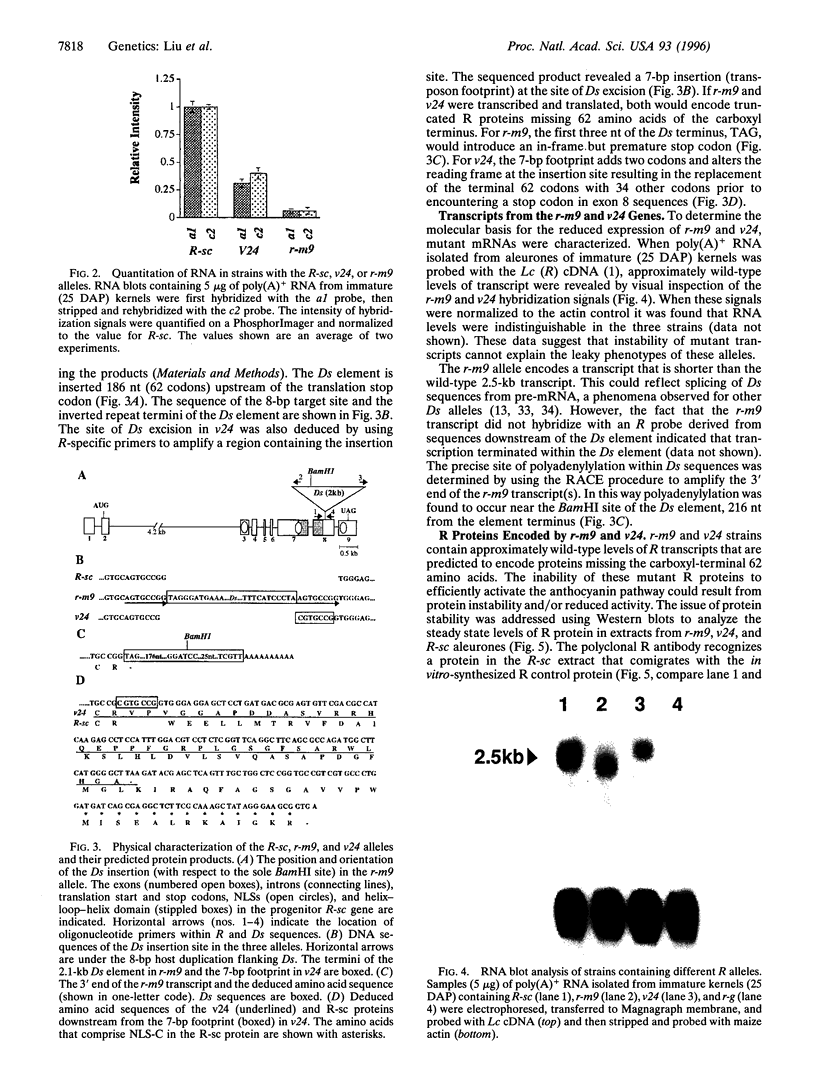
- Wessler S. R. The maize transposable Ds1 element is alternatively spliced from exon sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6192–6196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]