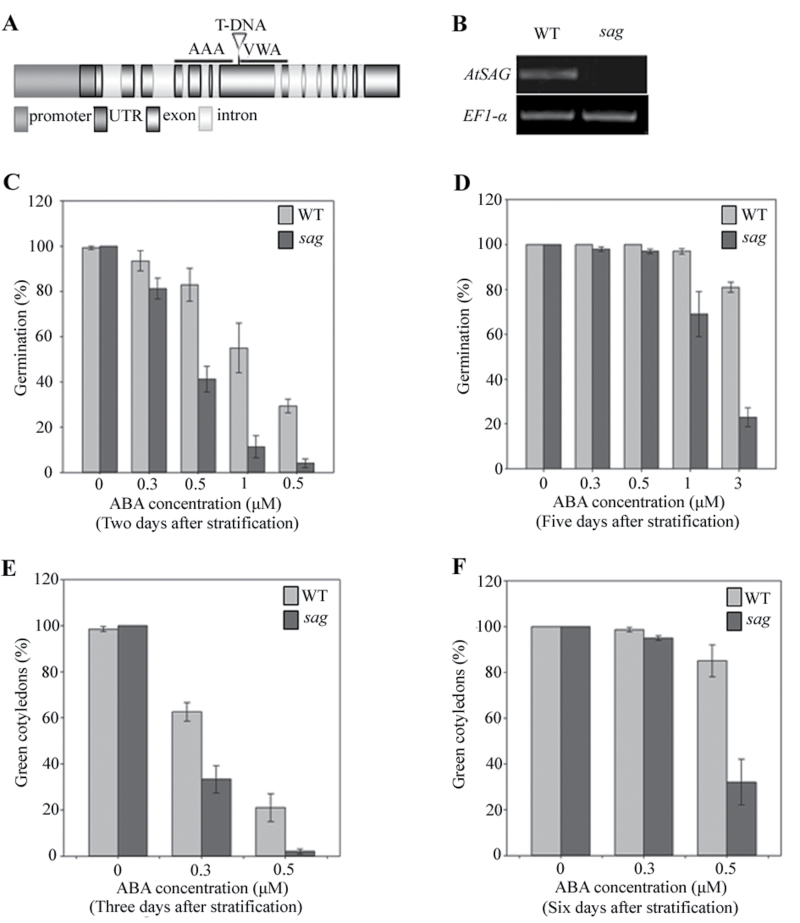
Fig. 1.
Characterization and ABA-responsive analysis of the T-DNA insertion mutant of sag plants. (A) T-DNA insertion site in sag; black boxes represent exons; white boxes represent introns; AAA and VWA represent the AAA and VWA domains in the putative peptide. (B) Reverse-transcription PCR analysis to confirm the knockout status of sag; upper panel shows AtSAG expression (35 cycles) in wild type (WT) and mutant line; lower panel shows EF1-α expression (25 cycles) as a control. (C and D) Seed germination records of WT and sag mutants treated with 0, 0.3, 0.5, 1.0, and 3.0 μM abscisic acid (ABA) at 2 and 5 d after stratification, respectively. (E and F) Cotyledon greening rates of the germinated seeds described in C and D with 0, 0.3, and 0.5 μM ABA at 3 and 6 d after stratification, respectively. Data are mean ± SD of at least three replicates; at least 100 seeds per genotype were counted in each replicate.